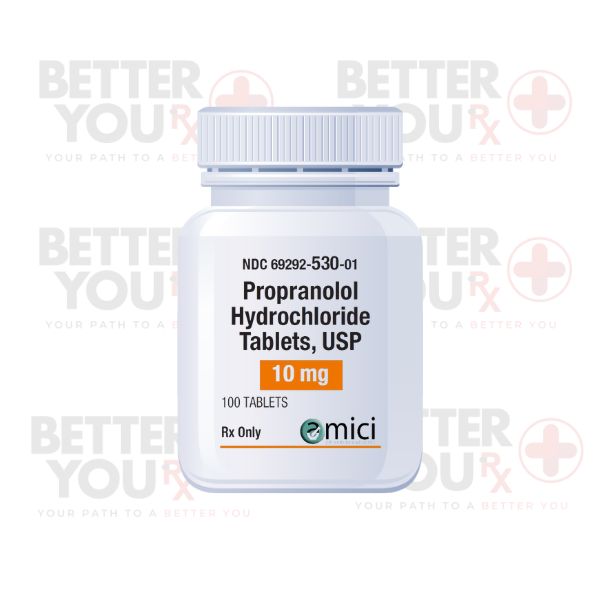
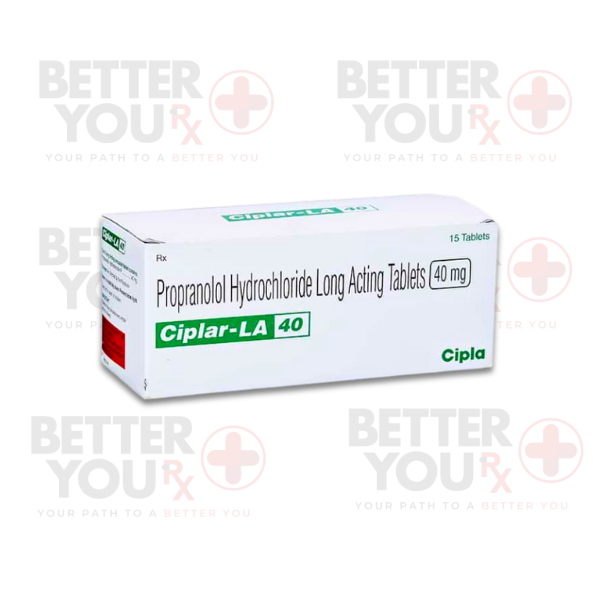
Indications:
●Management of hypertension (high blood pressure).
●Treatment and prevention of angina pectoris.
●Control of certain types of arrhythmias.
●Prevention of migraine headaches.
●Intervention in hyperthyroidism to manage symptoms.
●Management of anxiety and the physical symptoms related to it.
●Off-label use for performance anxiety.
Administration Guidelines
Oral Administration:
●Propranolol is administered orally in immediate-release tablets, long-acting capsules, and in liquid form. The dosing regimen is highly individualized, determined by the condition being treated, the patient's response, and the presence of co-administered medications.
●Healthcare providers often initiate therapy with a low dose and gradually increase it based on the patient's response and tolerance.
Dosage Forms:
●Immediate-release tablets, are often taken several times daily according to the prescribing information.
●Extended-release capsules are designed for once-a-day dosing to ensure steady blood medication levels.
Safety Preclusions
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
●The safety of propranolol during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been unequivocally established. Use during these periods should be carefully considered, weighing potential risks against benefits.
Long-term Use:
●Patients on long-term propranolol therapy require regular monitoring for signs of adverse effects, including assessments of heart function and blood pressure.
Drug Interactions:
●Propranolol interacts with a wide array of medications and substances, including, but not limited to, other blood pressure medications, antiarrhythmics, and certain antidepressants. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications and supplements they are taking to avoid potentially harmful interactions.
|