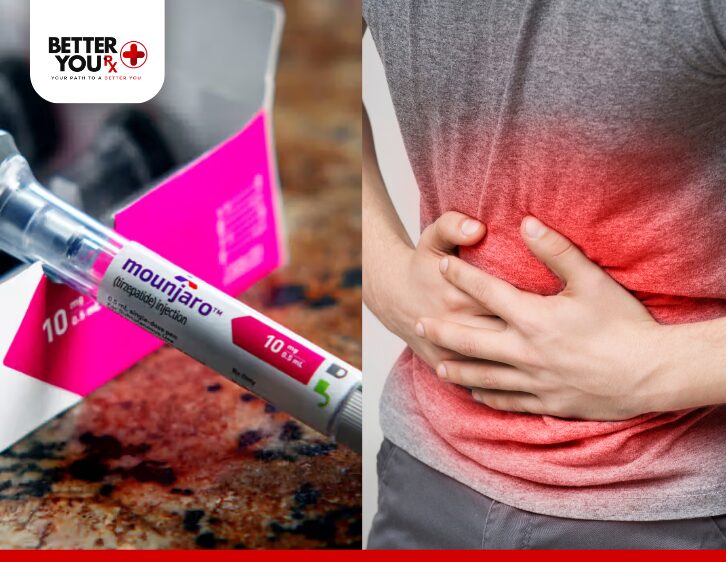
Can Mounjaro Cause Body Aches?
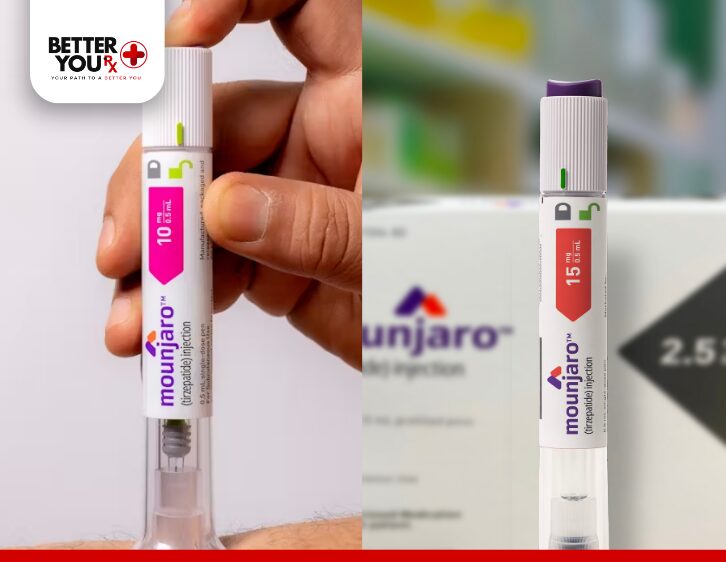
Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a medication used primarily for managing type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, for weight management. It works by stimulating insulin release and suppressing the production of glucagon, thus helping to regulate blood sugar levels. While Mounjaro offers significant benefits for patients with diabetes, like any medication, it can come with side effects. A common question from users is whether Mounjaro can cause body aches.
Body aches are not widely recognized as a common side effect of Mounjaro, but like with any medication, individuals may respond differently. This article explores the potential for body aches associated with Mounjaro, the possible mechanisms behind this symptom, and what you can do if you experience discomfort.
What Are the Common Side Effects of Mounjaro?

Before delving into body aches, it’s essential to understand the more common side effects of Mounjaro. These typically include gastrointestinal symptoms such as:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Decreased appetite
These side effects are most common at the beginning of treatment and usually lessen as your body becomes accustomed to the medication. However, body aches are not typically listed as a direct side effect of Mounjaro, so the relationship between Mounjaro and muscle or joint discomfort needs a deeper look.
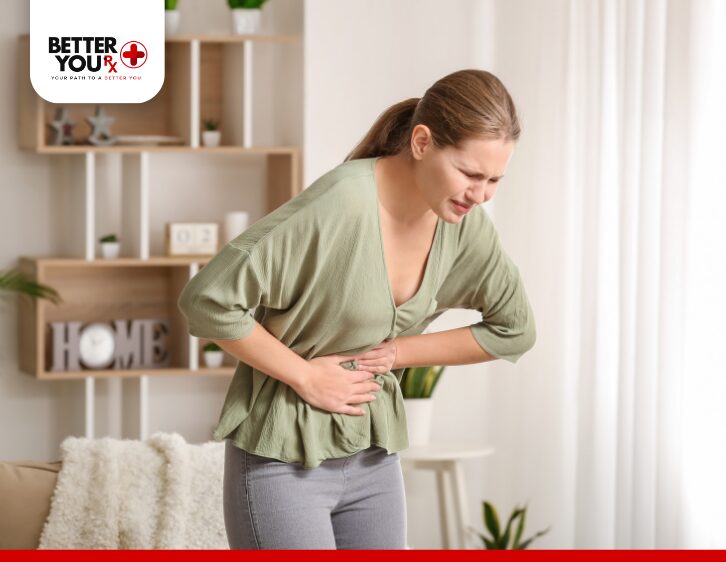
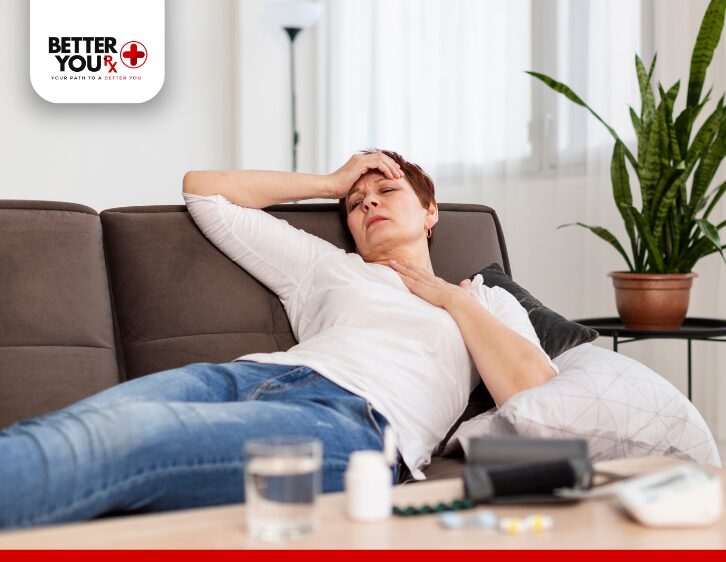
Can Mounjaro Cause Body Aches?
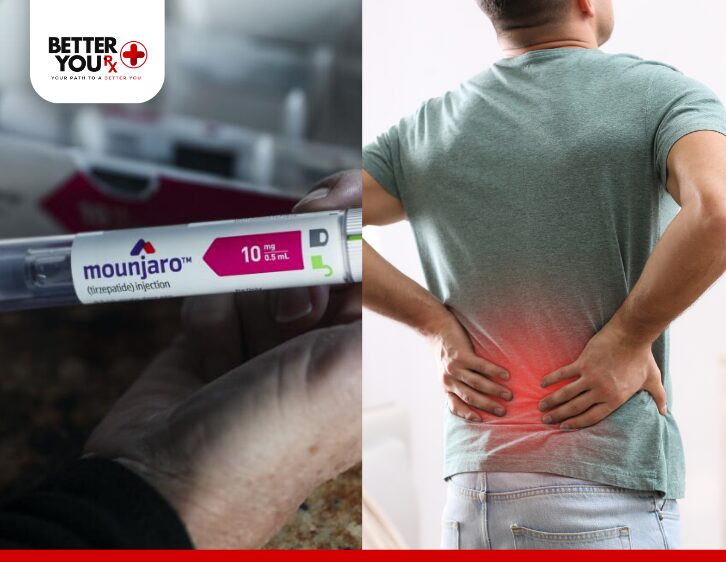
While not explicitly mentioned as a common side effect, there are several possible reasons why someone taking Mounjaro may experience body aches or discomfort.
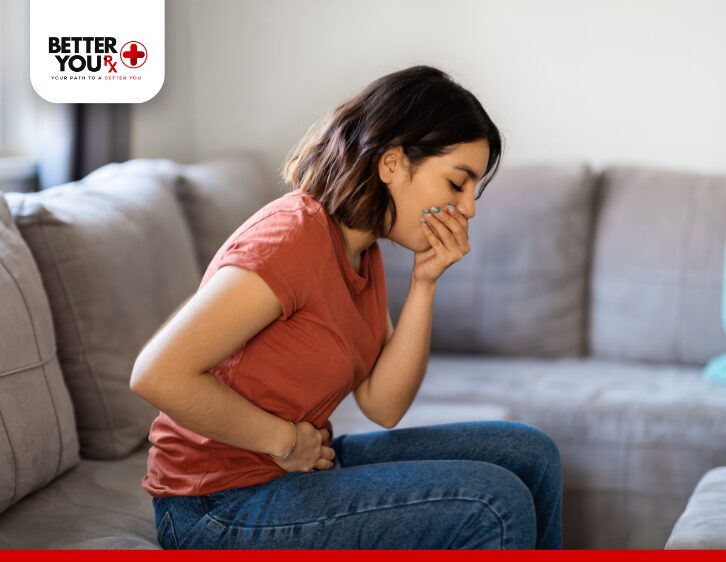
1. Dehydration from Gastrointestinal Symptoms
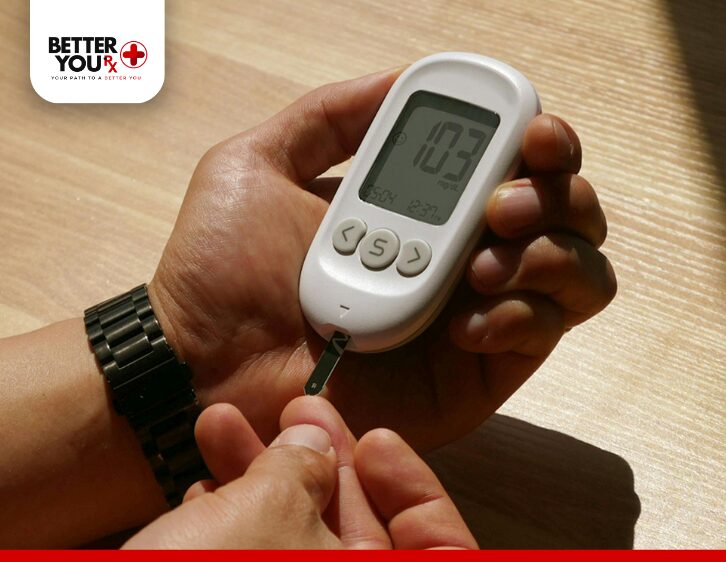
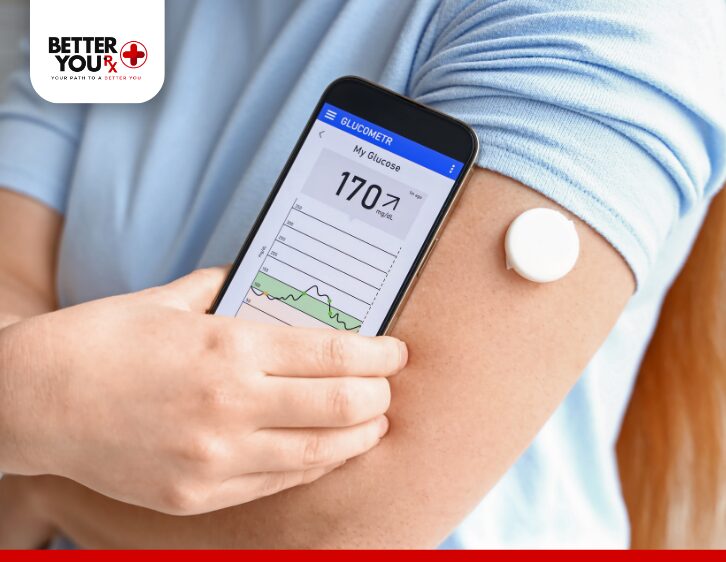
Mounjaro’s gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, are relatively common, particularly when a person first starts using the medication. These symptoms can lead to dehydration, which, in turn, may contribute to body aches, muscle cramps, and joint pain. Dehydration can affect how your muscles and joints function, leading to stiffness or discomfort.
2. Changes in Physical Activity Due to Weight Loss
Mounjaro is also known to assist with weight loss, which can lead to changes in a person’s physical activity levels. As weight decreases, individuals may become more active or start exercising to complement their weight loss journey. This increase in activity, especially if not done gradually, can cause muscle soreness or body aches, particularly in the early stages.
3. Adjustment to Medication
Whenever a person starts a new medication, especially one that impacts hormone levels, the body may go through an adjustment period. The process of your body adapting to Mounjaro’s effects on insulin and glucose metabolism could potentially trigger temporary muscle aches. However, this is not commonly reported and tends to subside as your body becomes accustomed to the drug.
4. Muscle or Joint Pain as a Rare Side Effect
While not typically listed as a side effect, some individuals may experience muscle or joint pain as a result of the medication’s broader impact on the body’s physiological processes. In rare cases, patients may report body aches as a result of their immune system’s reaction to the medication or other mechanisms that are not fully understood.
5. Medication Interactions
Mounjaro may interact with other medications you are taking. If you are using medications for other conditions such as high blood pressure, cholesterol, or other diabetes treatments, these interactions could contribute to muscle aches or discomfort. Some medications can also affect muscle function, and if combined with Mounjaro, this could lead to discomfort.
What Can You Do if You Experience Body Aches?
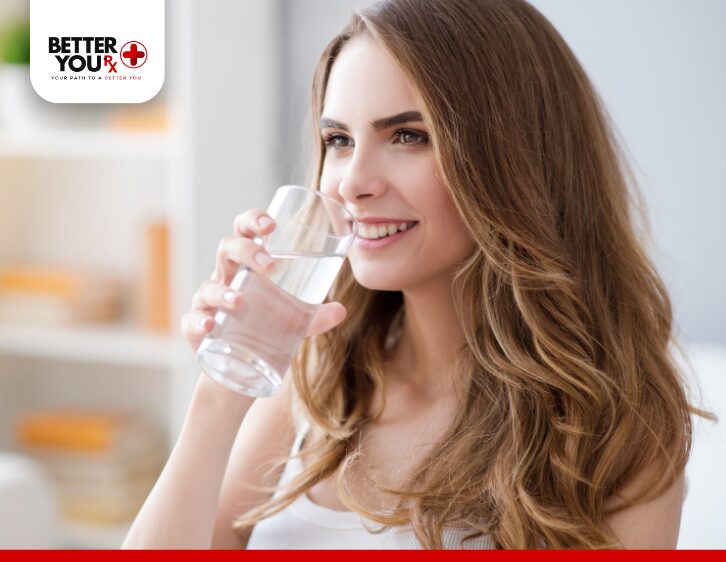

If you begin to experience body aches while using Mounjaro, it is essential to take proactive steps to alleviate the discomfort. Here are some helpful strategies:
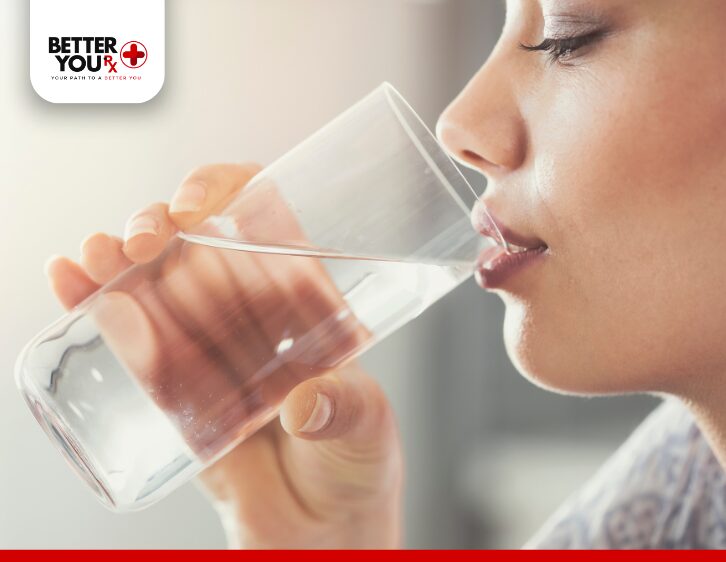
1. Hydrate Well
Since dehydration is a potential side effect of gastrointestinal symptoms, ensure you are drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated. Proper hydration can help alleviate muscle cramps, body aches, and other discomforts. It is also important to replace lost electrolytes if you’ve been experiencing vomiting or diarrhea.
2. Monitor Your Activity Level
If your body aches are related to increased physical activity or exercise, try to adjust your workout routine. Start with lighter activities and gradually build up intensity. This will give your muscles time to adjust to the changes, reducing the risk of overexertion and soreness.
3. Take Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
For mild body aches, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide temporary relief. However, always consult your healthcare provider before using any new medications to ensure they are safe to take alongside Mounjaro.
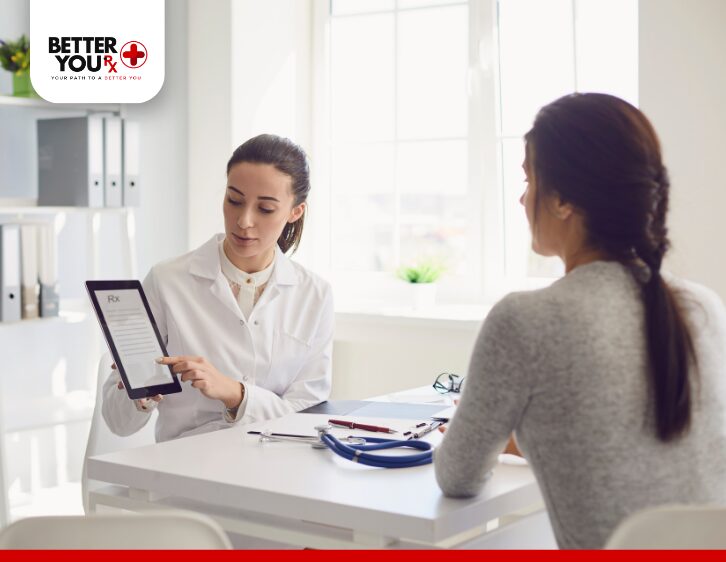
4. Consult Your Healthcare Provider
If the body aches persist or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as fever or swelling, it is important to consult your healthcare provider. They can help determine if the aches are related to Mounjaro or if another condition is at play. Your doctor may suggest adjusting your dosage, changing medications, or taking other steps to address the symptom.
5. Review Other Medications
If you are taking other medications along with Mounjaro, review them with your healthcare provider. Some drugs can cause muscle pain or discomfort when combined with Mounjaro. Your doctor can assess if any medication interactions may be contributing to the body aches and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Conclusion
Although body aches are not a common side effect of Mounjaro, some individuals may experience discomfort related to dehydration, changes in physical activity, or the body’s adjustment to the medication. If you experience body aches while using Mounjaro, it’s essential to stay hydrated, monitor your activity levels, and consult your healthcare provider if the discomfort persists. Always ensure that you are working closely with your doctor to manage any side effects and optimize your treatment plan.
By staying informed and proactive, you can better navigate any potential side effects and continue to benefit from the effectiveness of Mounjaro in managing your diabetes or weight loss.