How Stress Affects Blood Sugar Levels and What You Can Do About It
Stress is a natural response to life’s challenges, but for individuals living with diabetes, it can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Whether it’s due to work pressures, family problems, or health concerns, stress triggers biological responses that can make managing diabetes more difficult. Understanding how stress affects blood sugar levels and learning how to cope with it can make a big difference in your diabetes care.
How Stress Affects Blood Sugar Levels
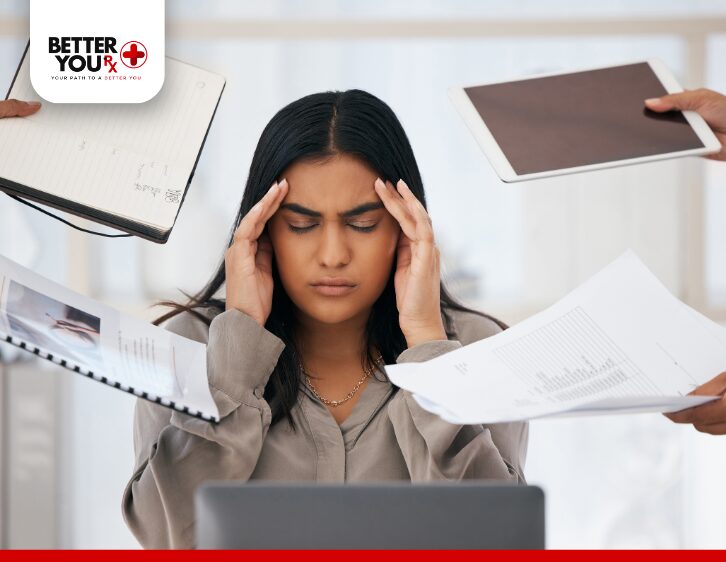

When you’re stressed, your body releases a series of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are part of the body’s “fight or flight” response, designed to help you react to immediate dangers. However, when stress is prolonged or chronic, it can lead to a number of changes in the body that affect your blood sugar levels.
- Increased Production of Glucose: Stress causes your body to release cortisol, a hormone that raises glucose levels in the blood. This happens because cortisol increases the production of glucose by the liver to prepare the body for action. While this is helpful in emergency situations, it can lead to higher blood sugar levels over time when stress is ongoing.
- Insulin Resistance: Chronic stress can make your body less responsive to insulin. Insulin is the hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. When stress is prolonged, your body may not respond to insulin as effectively, causing blood sugar levels to rise. This is particularly problematic for people with diabetes, as they may already struggle with insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production.
- Changes in Eating Habits: Stress can influence your eating patterns in unhealthy ways. Some individuals may turn to comfort food, often high in sugar or fat, as a way to cope with stress. This can cause a sudden spike in blood sugar levels. Others may experience a loss of appetite, potentially leading to missed meals, which can cause low blood sugar in people using insulin.
- Physical Reactions to Stress: Stress also impacts other areas of your body, like blood pressure, heart rate, and breathing. These reactions are designed to prepare your body to face a challenge, but over time, they can contribute to higher blood sugar levels, making diabetes harder to manage.
- Impact on Sleep: Chronic stress often leads to poor sleep quality or insomnia. Sleep is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels, as it helps your body restore and repair. Lack of sleep can increase insulin resistance and cause blood sugar levels to rise, further complicating diabetes management.
How to Manage Stress and Keep Blood Sugar Levels Stable

Managing stress is an essential part of maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Here are several strategies that can help reduce stress and keep your blood sugar under control:
1. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help calm your mind and reduce the physical impact of stress. Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment, which can help lower cortisol levels and reduce overall stress. Even taking a few minutes each day to focus on your breathing or practice meditation can make a big difference in how you feel and how your body responds to stress.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity

Exercise is one of the best ways to reduce stress while also helping control blood sugar levels. Physical activity increases the production of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Exercise also helps improve insulin sensitivity, so your body can better manage glucose levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate aerobic activity most days of the week. Walking, cycling, swimming, or yoga are all great options for managing stress.
3. Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep is crucial for managing both stress and blood sugar levels. Aim for 7–9 hours of restful sleep each night. Establishing a bedtime routine, avoiding caffeine and heavy meals before bed, and creating a peaceful sleep environment can improve your sleep quality and reduce stress.
4. Adopt Healthy Eating Habits
Managing your blood sugar levels is easier when you eat a balanced diet, even during stressful times. Stress can sometimes lead to emotional eating or skipping meals, which can cause fluctuations in blood sugar. Try to maintain a consistent eating schedule, focusing on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats. If you find yourself reaching for sugary snacks during stressful times, consider healthier alternatives like fruits, nuts, or yogurt.
5. Talk to Someone
Talking about your stress with someone you trust can help lighten the emotional load. Whether it’s a family member, friend, or therapist, sharing your concerns can provide emotional relief and reduce feelings of anxiety. Many people find that opening up about their stress helps them feel more in control and less overwhelmed.
6. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. These techniques involve consciously relaxing muscle groups or using mental imagery to create a calming experience. Incorporating these relaxation exercises into your routine can help keep stress levels in check.
7. Prioritize Self-Care
Taking time for yourself is an important part of stress management. Whether it’s reading a book, taking a bath, or enjoying a hobby, self-care activities can help you unwind and recharge. By prioritizing self-care, you’re better equipped to handle stress and maintain a positive mindset.
8. Set Realistic Expectations
Managing diabetes can be overwhelming, especially when you’re also dealing with stress. Setting realistic goals and expectations for yourself can help reduce stress and give you a sense of control. Break tasks down into smaller, manageable steps and celebrate small successes along the way.
9. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol Intake
Caffeine and alcohol can exacerbate stress and interfere with blood sugar control. Excessive caffeine can lead to increased anxiety, while alcohol can cause blood sugar to drop too low or spike unpredictably. Try limiting your intake of these substances, especially during stressful times, to help keep your blood sugar stable.
10. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can make stress worse and cause blood sugar levels to rise. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help keep you hydrated and support your body’s ability to cope with stress. Avoid sugary drinks or excessive amounts of caffeine, as these can negatively affect blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Stress is an inevitable part of life, but its effects on blood sugar levels can be managed with the right strategies. By incorporating stress-reduction techniques, regular physical activity, and healthy eating habits, you can help keep your blood sugar levels stable while minimizing the impact of stress on your diabetes. If you find that stress is becoming overwhelming or interfering with your diabetes management, consider reaching out to a healthcare provider or mental health professional for additional support.
Taking steps to reduce stress not only helps with blood sugar control but also promotes overall well-being, making it easier to live a healthy and balanced life with diabetes.