Ozempic and Semaglutide Guide for 2025: What You Need to Know
Key Takeaways
- Ozempic and semaglutide offer powerful benefits for blood sugar control and weight loss.
- Weekly injections are easy to manage with proper guidance and technique.
- Side effects are usually mild, but should be monitored.
- Better You Rx offers secure, affordable access to Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelsus.
- These medications are best used as part of a broader lifestyle plan, including diet and exercise.
In 2025, Ozempic and semaglutide will continue to dominate the landscape of modern healthcare—particularly for individuals managing type 2 diabetes and seeking sustainable weight loss. As GLP-1 receptor agonists, these medicines are altering the method we tactic metabolic health.
Whether you’re just starting your journey or looking to optimize your treatment plan, this guide covers everything from how these medications work to who should take them, how to use them safely, and where to buy them online.
“Consistency and proper guidance are the cornerstones of any successful semaglutide therapy—don’t go it alone, work with trusted professionals.”
If you’re ready to explore safe, verified access to these medications, Better You Rx offers both Ozempic and related GLP-1 options through a secure and supportive pharmacy experience.
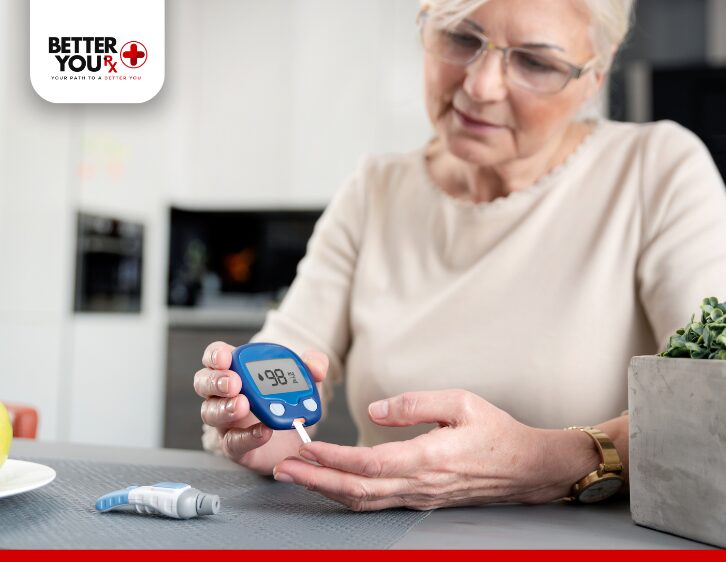
How Ozempic and Semaglutide Work for Diabetes and Weight Loss

Both Ozempic and semaglutide work by mimicking a natural hormone called GLP-1, which helps regulate insulin, slow digestion, and suppress appetite. Here’s how they function:
- For Type 2 Diabetes: They lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin release and reducing glucagon secretion after meals.
- For Weight Loss: By slowing gastric emptying and curbing hunger, they reduce calorie intake and support gradual fat loss.
This dual impact makes them incredibly effective for both glycemic control and metabolic weight management. According to a clinical study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH.gov), semaglutide showed superior results in reducing A1C and weight compared to many conventional therapies.
Benefits of Ozempic and Semaglutide in 2025

The rise of semaglutide for weight loss and diabetes management isn’t just hype—it’s backed by clinical success. Patients using these medications consistently report improvements far beyond just blood sugar control.
Top Benefits:
- Effective glycemic regulation for type 2 diabetes.
- Reduced hunger and calorie intake.
- Sustained weight loss of 10–15%
- Better cardiovascular health, counting subordinate blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Lower risk of major heart events.
These advantages position Ozempic and semaglutide as leading tools in managing metabolic syndrome and related conditions.
Ozempic vs Semaglutide: Are They the Same?
One of the most searched comparisons in 2025 is semaglutide vs. Ozempic. Here’s the truth:
- Semaglutide is the active ingredient.
- Ozempic is a proprietary injectable medication, characteristically used for type 2 diabetes.
- Wegovy is the same compound, dosed for weight loss.
- Rybelsus is an oral semaglutide for blood sugar control.
Each has unique use cases but shares the same metabolic foundation. You can find all these products through Better You Rx—a Canadian pharmacy online offering safe access to essential medications.
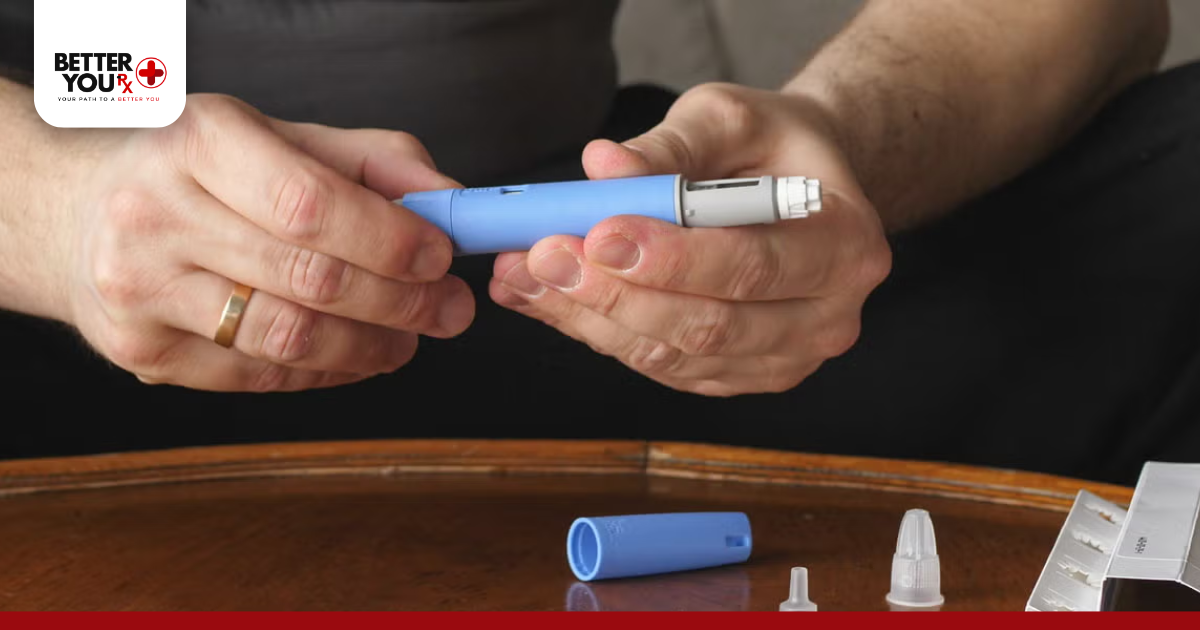
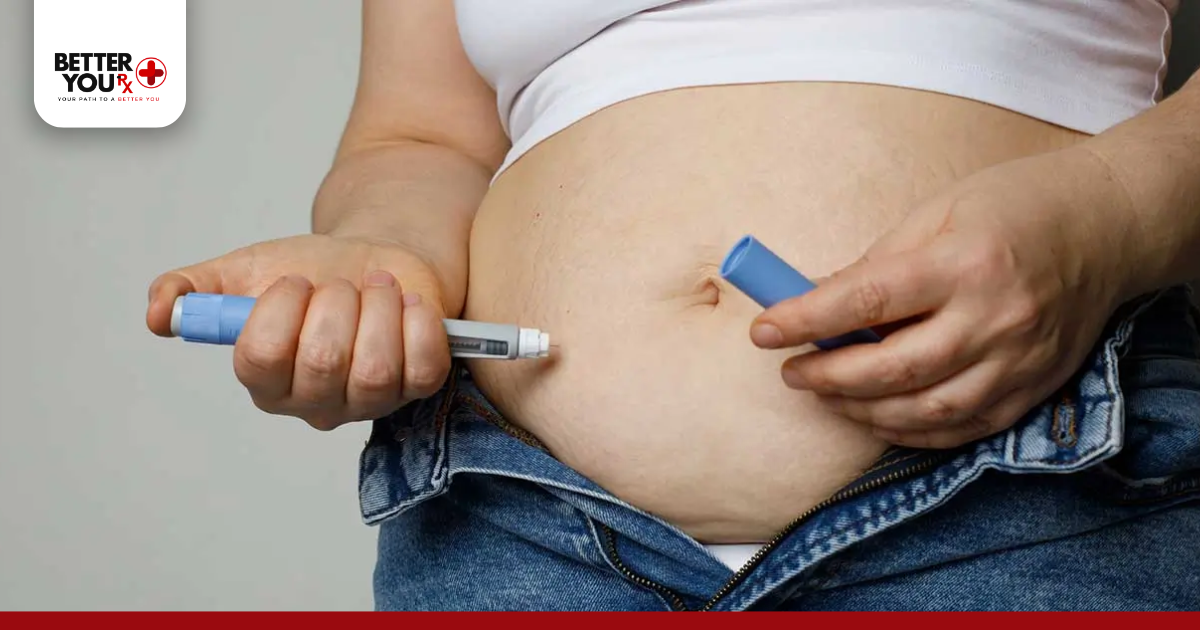
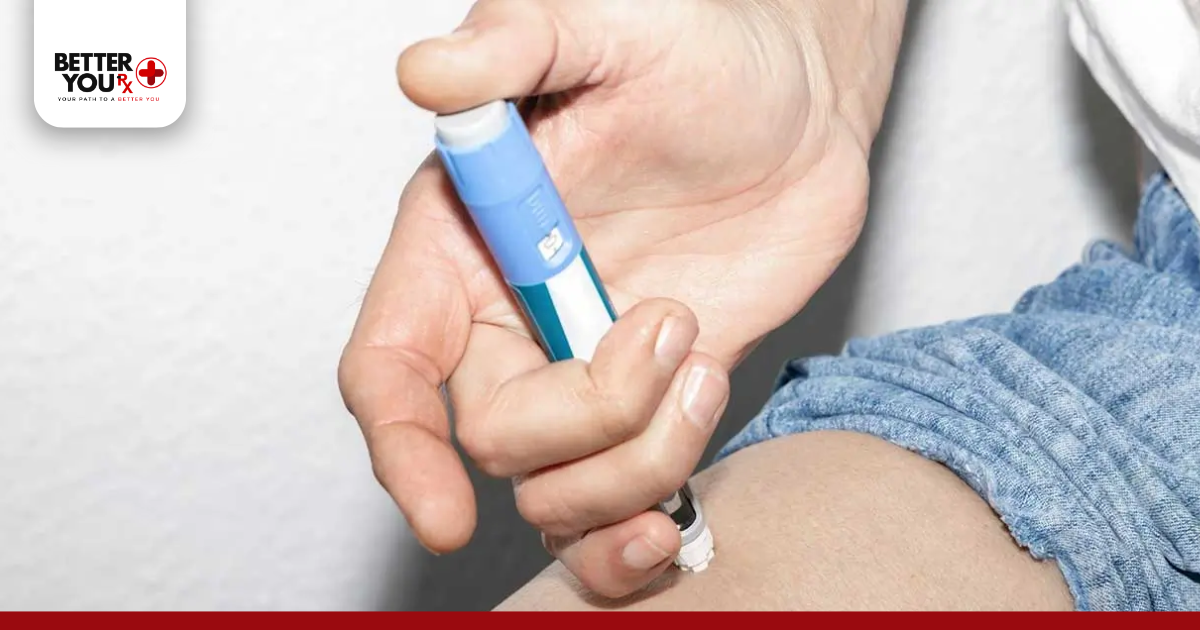
How to Take Semaglutide Safely
If you’re inquisitive about how to take semaglutide, the response is frank but dangerous:
- Once-weekly injection, same day each week.
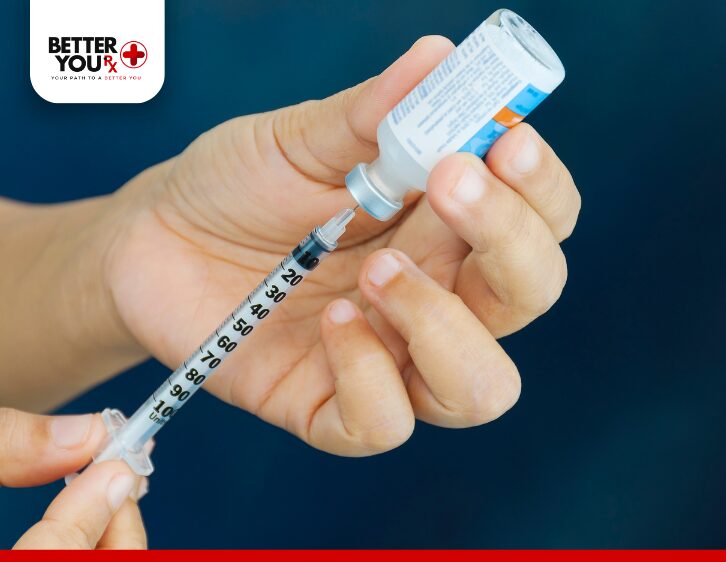
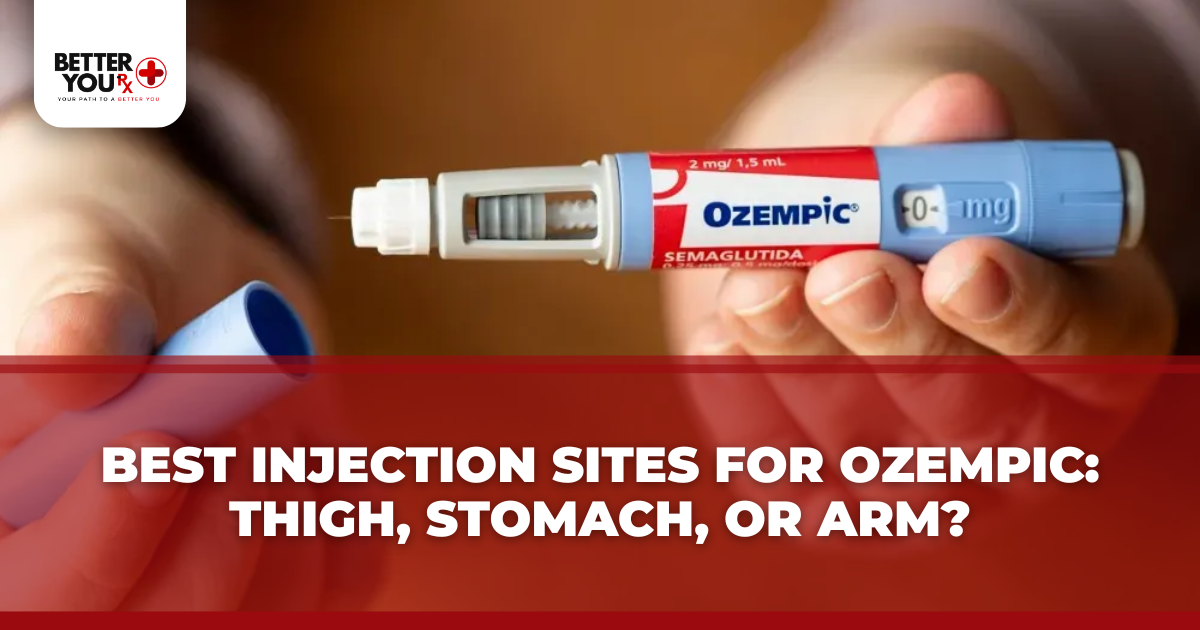
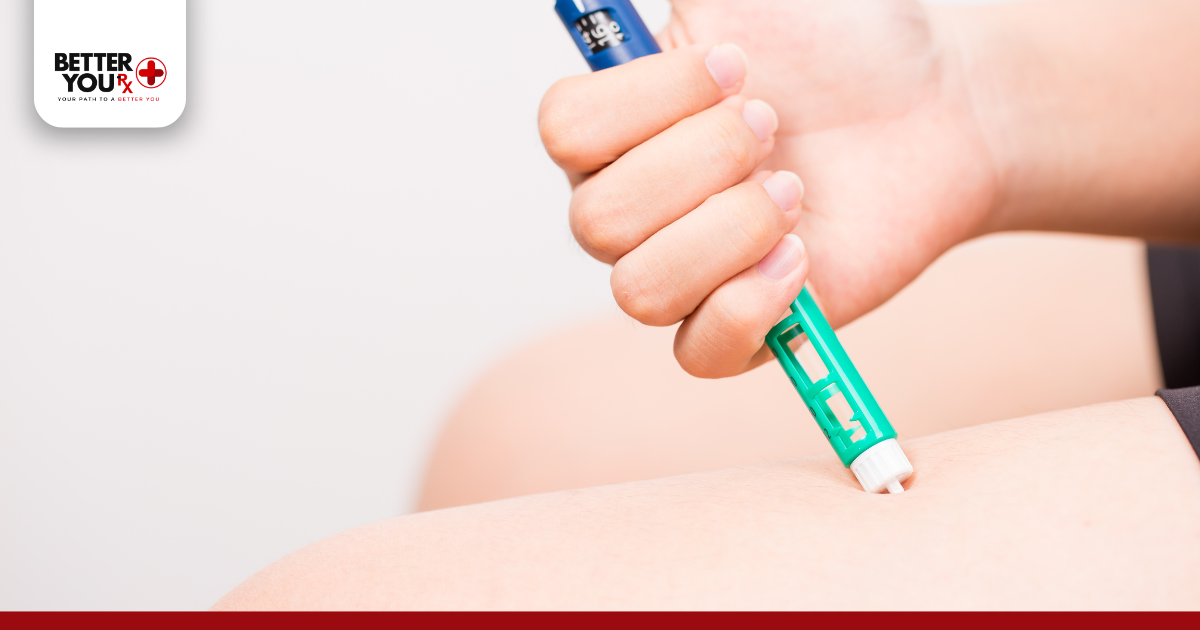
- Sites: Inject into the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm.
- Rotate locations to avoid irritation.
Helpful Tip: “The best time to take semaglutide is the time you’ll remember consistently.” Whether it’s Monday morning or Sunday night, routine builds results.”
Looking for a detailed breakdown on how to inject Ozempic? The Health Tips section at Better You Rx provides step-by-step guides and expert advice.
Ozempic Dosage for Weight Loss
Your Ozempic dosage for weight loss typically starts at 0.25 mg per week, gradually increasing to 1.0 mg or more, based on how well you respond. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions, especially when transitioning from other GLP-1s like Wegovy or Rybelsus.
For secure, prescription-based access to these options, explore Better You Rx’s wide range of medications through their best Canadian online pharmacy portal.
Ozempic Side Effects and Safety Considerations

While highly effective, Ozempic and semaglutide are not without potential side effects. It’s essential to appreciate these dangers earlier start treatment.
Common Side Effects:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea.
- Headache
- Decreased appetite
These typically appear during the first few weeks and often subside as the body adjusts.
Less Common but Serious Risks:
- Pancreatitis
- Kidney complications
- Gallbladder issues
- Possible thyroid tumors (in animal studies)
So, is Ozempic safe? For most patients, yes, when prescribed and monitored by a healthcare provider. It’s not recommended for individuals with:
- A history of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Type 1 diabetes
- Severe gastrointestinal conditions.
For detailed safety guidance, see the CDC’s diabetes treatment resource:
🔗 CDC – Diabetes Basics and Treatment
Who Should Use Ozempic and Semaglutide in 2025?
These medications are ideal for:
- Adults with type 2 diabetes needing better glycemic control.
- People with a BMI ≥ 30, or ≥ 27 with a weight-related condition.
- Those who haven’t succeeded with diet/exercise alone.
They are not suitable for:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals
- Patients with a personal or family history of thyroid cancer.
- Type 1 diabetics or individuals with a history
For guidance tailored to your health profile, Better You Rx offers professional support and a full portfolio of GLP-1 medications.
Informed Use Starts with Trusted Resources.
Ozempic and semaglutide are changing lives in 2025—offering real, sustainable solutions for those battling type 2 diabetes or weight challenges. These medications do more than suppress hunger—they support long-term metabolic health, when used responsibly.
Partnering with a trustworthy provider like Better You Rx ensures you’re receiving real medications, expert insights, and affordable pricing. Whether you’re new to semaglutide therapy or refining your regimen, knowledge is your first prescription.
FAQs: Quick Answers About Ozempic and Semaglutide
How to take semaglutide?
Administer once-weekly injection.
What’s the best time to take semaglutide?
Pick a consistent day each week, ideally tied to a routine or reminder.
How do Ozempic and semaglutide assist with weight loss?
They reduce appetite and delay digestion, leading to sustained calorie reduction and fat loss.
What’s the difference between semaglutide and Ozempic?
Semaglutide is the ingredient; Ozempic is one of the brand-name drugs covering it.
Where can I buy Ozempic safely online?
Trusted platforms like Better You Rx ensure secure prescriptions and verified products.













 Diabetes
Diabetes