Wegovy vs Ozempic: Which Semaglutide Option Is Right for You in 2025?
Key Takeaways
- Wegovy: Designed for weight loss with a higher semaglutide dosage.
- Ozempic: Primarily for type 2 diabetes management.
- Cost: Wegovy is generally more expensive than Ozempic.
Insurance: Coverage varies; consult your provider. - Consultation: Always discuss with a healthcare professional before starting treatment.
If you’re exploring GLP-1 medications for weight loss or type 2 diabetes, the debate between Wegovy vs Ozempic is more relevant than ever. Both drugs share the same active ingredient—semaglutide—but serve different treatment goals.
Whether you’re focused on managing your blood sugar or targeting substantial fat loss, understanding how these two medications differ in dosage, application, cost, and insurance coverage can help you make an informed decision.
“Choosing between Wegovy and Ozempic isn’t just about weight loss—it’s about selecting the right dosage, purpose, and support system to reach your health goals safely.”
To access either medication through a trusted Canadian pharmacy affiliate, check out Better You Rx, where you’ll find semaglutide options like Wegovy and Ozempic)—delivered reliably and affordably.
Understanding Wegovy and Ozempic: The Same Ingredient, Different Goals

Both Wegovy and Ozempic contain semaglutide, a powerful GLP-1 receptor agonist that works by:
- Stimulating insulin release
- Suppressing glucagon (a hormone that raises blood sugar)
- Slowing gastric emptying to increase fullness and reduce calorie intake
But here’s the key difference:
- Wegovy for weight loss is government-approved specifically for obesity treatment
- Ozempic for type 2 diabetes is approved primarily for glycemic control, with weight loss as a secondary benefit
In the next section, we’ll compare dosage strategies and effectiveness—highlighting why Ozempic weight loss vs Wegovy results vary based on intent and formulation.
Wegovy for Weight Loss: Higher Dosage, Stronger Results

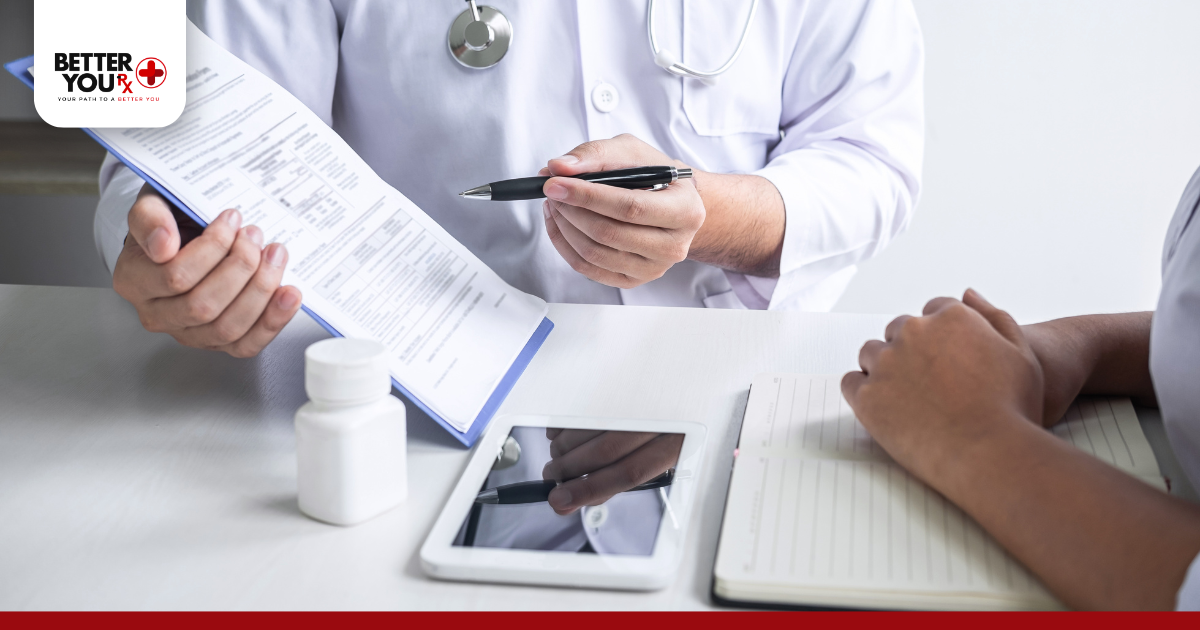
Wegovy was approved by the U.S. government specifically for the treatment of obesity. It’s prescribed to adults with a BMI of 30 or higher—or 27 with weight-related conditions like high blood pressure or sleep apnea.
The semaglutide dosage in Wegovy starts low and gradually increases to a maintenance dose of 2.4 mg weekly, allowing the body to adjust while maximizing appetite suppression and fat loss.
Clinical Results
According to a government-backed STEP 1 clinical trial, adults using Wegovy (semaglutide) lost an average of 14.9% of their body weight over 68 weeks, compared to just 2.4% in the placebo group. This large, randomized study included 1,961 participants with obesity or weight-related health conditions and confirms Wegovy’s strong efficacy as a medical weight loss treatment.
If your primary goal is sustainable weight reduction, Wegovy’s higher semaglutide dosage may make it more effective than Ozempic.
Ozempic for Type 2 Diabetes (and Some Weight Loss)
Ozempic is primarily prescribed for type 2 diabetes, targeting blood sugar regulation through semaglutide’s effect on insulin and digestion.
Patients begin with a 0.25 mg weekly dose, which gradually increases—typically up to 2.0 mg. In some off-label cases for weight loss, it may reach 2.4 mg, similar to Wegovy.
While Ozempic weight loss vs Wegovy outcomes are still meaningful, the results tend to be slightly more modest due to the lower dosing structure and different treatment focus.
Wegovy vs Ozempic Side Effects: What’s the Difference?

Both medications share similar side effects due to their semaglutide base. These include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fatigue
- Headaches
More serious but rare risks include:
- Pancreatitis
- Gallbladder issues
- Possible thyroid complications
- Vision-related conditions like NAION (as noted in recent government-funded studies)
There’s also the cosmetic concern commonly referred to as “Ozempic butt”—sudden weight loss leading to sagging skin. It’s not caused by the drug itself but by rapid fat reduction. Mitigation strategies include:
- Strength training
- Adequate protein intake
- Hydration and gradual progress
Wegovy vs Ozempic Cost: What to Expect in 2025
As of 2025, the out-of-pocket costs for these medications vary significantly:
- Wegovy: Approximately $1,349 per month without insurance.
- Ozempic: Approximately $935 per month without insurance.
Insurance coverage can reduce these costs substantially, but it’s important to note that coverage for weight loss medications like Wegovy is often limited.
For those seeking affordable options, Better You Rx offers access to semaglutide-based treatments through a trusted Canadian pharmacy affiliate.
Insurance Coverage for Wegovy and Ozempic in 2025
Insurance coverage for these medications varies:
- Ozempic: Generally covered when prescribed for type 2 diabetes management.
- Wegovy: Coverage is less common, especially when prescribed solely for weight loss.
Patients are advised to consult with their insurance providers to understand their specific coverage options.
Which Is Better: Ozempic or Wegovy?
The choice between Ozempic and Wegovy depends on individual health goals:
- Wegovy: More effective for significant weight loss due to its higher semaglutide dosage.
- Ozempic: Primarily used for type 2 diabetes management, with weight loss as a secondary benefit.
Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the most appropriate treatment based on personal health needs.
Making an Informed Choice Between Wegovy and Ozempic
Choosing between Wegovy and Ozempic hinges on your specific health goals—be it significant weight loss or managing type 2 diabetes. Understanding the differences in dosage, cost, and insurance coverage is crucial.
For those seeking access to these medications through a reliable source, Better You Rx provides options via a trusted Canadian pharmacy affiliate, ensuring affordability and convenience.
FAQs: Wegovy vs Ozempic
Q: How effective is Wegovy compared to Ozempic for weight loss?
A: Wegovy has shown greater weight loss results due to its higher dosage of semaglutide.
Q: Are the side effects of Wegovy and Ozempic different?
A: Both medications share similar side effects, including nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
Q: Is Wegovy covered by insurance?
A: Coverage varies; it’s often limited when prescribed solely for weight loss.
Q: Can I switch from Ozempic to Wegovy?
A: Switching should be done under medical supervision to ensure safety and efficacy.