Why Rybelsus as Oral Semaglutide Might Be Your Best Choice Over Injectables
When managing weight and controlling blood sugar, semaglutide has become a popular choice. Traditionally, this medication has been available in injectable forms like Wegovy and Ozempic. Now, it’s also offered as an oral medication called Rybelsus. Many people find the idea of taking a pill rather than getting injections appealing. But how does Rybelsus compare to its injectable versions, and why might it be your better option?
In this article, we’ll dive into how Rybelsus stacks up against the injectables and why it could be a great choice for your weight management and blood sugar control needs.
What is Rybelsus?
Rybelsus is an oral medication that features semaglutide, which is a type of drug called a GLP-1 receptor agonist. Unlike other semaglutide options that are administered through injections, Rybelsus comes in a convenient pill form. This makes it an appealing choice for those who prefer not to deal with injections.
Semaglutide, the active ingredient in Rybelsus, works by mimicking the effects of a natural hormone in the body known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). This hormone is vital for managing both appetite and blood sugar levels. By activating GLP-1 receptors, Rybelsus helps to manage weight and improve blood sugar control.
Rybelsus is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it aids in lowering blood sugar levels and can support weight loss. The pill form of Rybelsus offers a less invasive alternative to injectable medications, making it easier for many people to incorporate into their daily routine.
Overall, Rybelsus provides a practical option for managing both weight and blood sugar levels, especially for those who are looking for a non-injection-based treatment.
How Rybelsus Works
Mechanism of Action:
- Appetite Control: Rybelsus works by mimicking the effects of GLP-1, a hormone that helps regulate appetite. This action helps you feel fuller for longer and reduces overall food intake.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: It helps control blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin secretion and reducing the production of glucose in the liver.
- Digestive Process: Rybelsus slows down the emptying of the stomach, which also contributes to a prolonged feeling of fullness and helps manage food cravings.
Benefits of Rybelsus Over Injectables

No Needles: A Key Benefit of Rybelsus
One of the standout features of Rybelsus is its oral administration, which means you can take it in pill form rather than needing to use injections. This aspect of Rybelsus is particularly significant for several reasons:
- Comfort and Convenience: For many people, the thought of needles can be uncomfortable or even anxiety-inducing. Rybelsus offers a much more comfortable alternative by eliminating the need for frequent injections. This can make managing your condition less stressful and more convenient.
- Simplified Medication Routine: With Rybelsus, you don’t have to worry about the logistics of injecting yourself. This can simplify your medication routine, as you only need to remember to take a pill daily. It also removes the need for additional supplies like syringes, which can be cumbersome and require proper disposal.
- Increased Adherence: Oral medications often have higher adherence rates compared to injectable forms. The ease of taking a pill can lead to better consistency in following the prescribed treatment plan. This improved adherence can contribute to more effective management of your weight and blood sugar levels.
- Less Disruption: Injecting medication can be time-consuming and might require adjustments to your daily routine, such as finding a private space to administer the injection. Taking a pill, on the other hand, can be seamlessly integrated into your daily life, making it easier to stay on track with your treatment.
- Avoids Injection Site Reactions: Injectable medications can sometimes cause reactions at the injection site, such as irritation or pain. Rybelsus avoids these issues altogether since it’s taken as a pill.
Effectiveness

Comparable Results
Rybelsus has demonstrated strong effectiveness in managing both weight and blood sugar levels, comparable to its injectable counterparts like Wegovy and Ozempic. Clinical studies and real-world use have shown that Rybelsus can significantly reduce body weight and improve glycemic control for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Management: Similar to injectable semaglutide products, Rybelsus helps reduce body weight by curbing appetite and enhancing feelings of fullness. Research indicates that individuals using Rybelsus can achieve substantial weight loss, making it an effective tool for weight management. This weight loss is achieved through the medication’s action on GLP-1 receptors, which helps regulate hunger and caloric intake.
- Blood Sugar Control: Rybelsus is also effective in managing blood sugar levels. It works by mimicking the action of GLP-1, a hormone that helps regulate insulin and glucose levels. By enhancing insulin release and reducing glucose production, Rybelsus helps stabilize blood sugar levels. This effectiveness in controlling blood sugar is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it helps prevent the complications associated with poor glycemic control.
Flexibility
Rybelsus offers a flexible and convenient alternative for those who might struggle with injectable medications.
- Ease of Use: Unlike injectable forms, Rybelsus comes in a pill form, which many find easier to integrate into their daily routine. There’s no need to master injection techniques or adhere to strict schedules for injections. This can be especially beneficial for individuals who are uncomfortable with needles or have difficulty with self-injection.
- Simplified Routine: Taking Rybelsus as a daily oral medication simplifies the treatment process. It eliminates the need for specialized storage and handling of injectable supplies. This simplicity can lead to better adherence to the treatment regimen, as the medication is easier to take regularly and consistently.
- Accessibility: For some people, the ability to take medication orally can be more accessible, particularly for those who travel frequently or have busy lifestyles. Rybelsus offers a straightforward and effective option for managing health conditions without the logistical challenges of injections.
Considerations When Choosing Rybelsus
Dosage and Administration
Daily Pill: Rybelsus is typically taken once daily. It’s important to follow the prescribed dosage and timing to ensure optimal effectiveness.
Food Interactions: Rybelsus should be taken on an empty stomach with a small amount of water, and you should wait at least 30 minutes before eating or drinking anything else.
Side Effects
Gastrointestinal Issues: Some people may experience gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or diarrhea, when starting Rybelsus. These effects are generally mild and may diminish with time.
Monitoring: As with any medication, monitoring for side effects and regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential.
Cost and Accessibility
Availability: Ensure that Rybelsus is available through your pharmacy or healthcare provider.
Why Choose Rybelsus?

Rybelsus offers a range of advantages that make it an appealing alternative to injectable semaglutide products. One of its most significant benefits is convenience. As an oral medication, Rybelsus eliminates the need for needles, making the process of managing weight and blood sugar levels simpler and less invasive. This needle-free administration can be particularly advantageous for individuals who experience anxiety or discomfort with injections. The ease of taking a daily pill, without the need for syringes or special techniques, often leads to improved adherence and consistency in treatment.
However, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Rybelsus is the right choice for you. They can provide personalized advice based on your health needs and goals, ensuring that Rybelsus aligns with your specific treatment plan.
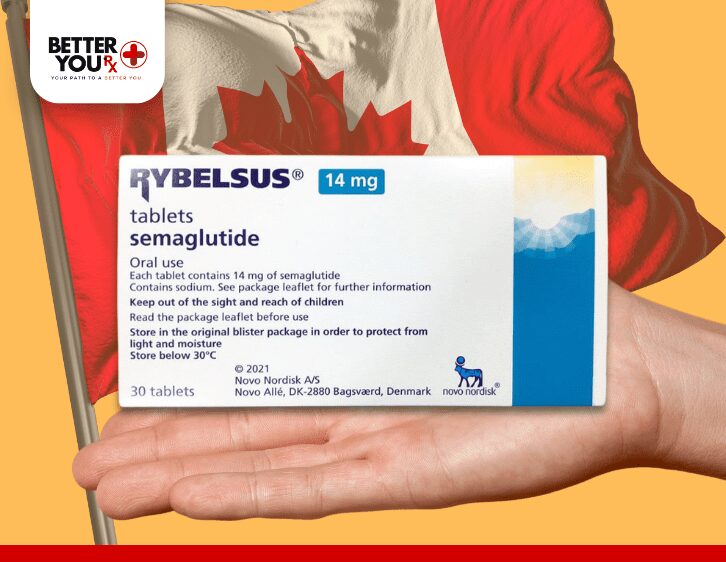
Better You Rx offers Rybelsus through our network of Canadian pharmacies, making it easy to access this effective treatment option. As a pharmacy-affiliated referral service, we ensure competitive prices and support to help you achieve your health and weight management goals. Explore your options with Better You Rx and take a proactive step toward managing your health with Rybelsus.