Can You Take Phentermine with Ozempic?
The use of medications for weight loss and diabetes management is increasingly common as the prevalence of obesity and diabetes continues to rise. Among the options available, phentermine and Ozempic (semaglutide) are two widely used drugs. While phentermine is primarily an appetite suppressant, Ozempic is a GLP-1 receptor agonist that regulates blood sugar levels and supports weight loss. But can these two medications be used together? This article explores the potential interactions, benefits, and risks of combining phentermine and Ozempic.
Understanding Ozempic
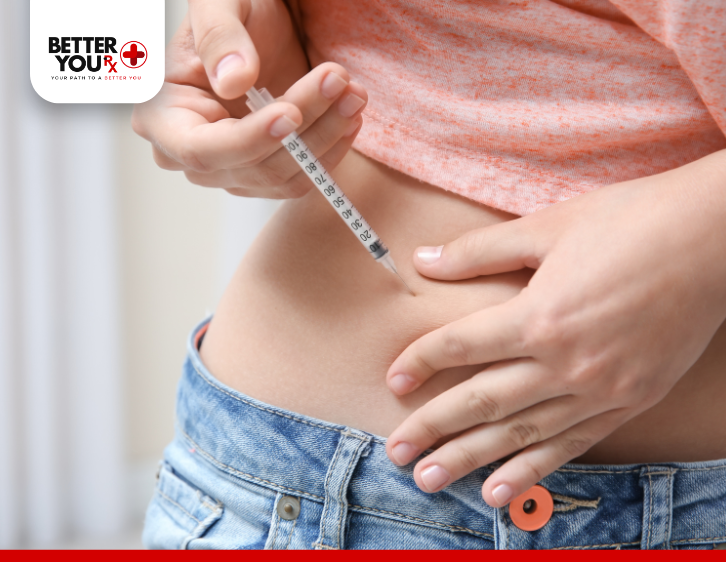
Ozempic, with the active ingredient semaglutide, is a medication used to manage type 2 diabetes and aid in weight loss. It works by mimicking the effects of the GLP-1 hormone, which slows gastric emptying, enhances insulin secretion, and reduces appetite. This dual-action mechanism makes it effective for controlling blood sugar levels and promoting sustainable weight loss. Ozempic is typically administered as a once-weekly injection and has gained popularity due to its efficacy.
Understanding Phentermine

Can You Take Phentermine with Ozempic?
The combination of phentermine and Ozempic is not uncommon, as their mechanisms of action are different and could theoretically complement each other. While Ozempic focuses on regulating blood sugar and reducing appetite through hormonal pathways, phentermine primarily suppresses appetite via the central nervous system. Together, they may enhance weight loss efforts in specific cases. However, there are important considerations and potential risks associated with their combined use.
Potential Drug Interactions
Moderate Interaction: Phentermine and Ozempic
One significant concern when combining phentermine and Ozempic is the potential need for adjustments in diabetic treatment. As patients lose weight with phentermine, their insulin sensitivity may improve, potentially lowering their blood sugar levels. This could necessitate changes in the dosage of Ozempic or other diabetic medications. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is a potential risk, with symptoms including:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Nervousness or confusion
- Tremors
- Nausea
- Hunger
- Weakness
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
Patients should inform their healthcare provider if they experience these symptoms, as frequent monitoring and adjustments may be required.
Drug and Food Interactions
Phentermine should not be combined with alcohol, as it increases the risk of cardiovascular and nervous system side effects such as:
- Increased heart rate
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Depression or difficulty concentrating
Similarly, Ozempic may affect the absorption of other oral medications due to its impact on gastric emptying. While this interaction may not always be significant, individuals should consult their healthcare provider to ensure their other medications are not adversely affected.
Benefits of Combining Phentermine and Ozempic
For some individuals, the combination of these medications may provide enhanced benefits, particularly for weight loss. Phentermine’s appetite suppression combined with Ozempic’s effects on appetite, blood sugar, and metabolic processes could create a synergistic effect. This combination might be appropriate in carefully monitored scenarios where the benefits outweigh the risks.
Risks of Combining Phentermine and Ozempic

Overlapping Side Effects
Both medications may lead to side effects, including nausea, dizziness, and a heightened heart rate. When used together, these side effects may be exacerbated. Other risks include:
- Cardiovascular strain from phentermine’s stimulant effects
- Hypoglycemia due to improved insulin sensitivity
- Gastrointestinal discomfort from Ozempic’s delayed gastric emptying
Limited Research
There is currently limited clinical research on the combined use of phentermine and Ozempic. Without robust studies, the safety and efficacy of this combination remain uncertain, emphasizing the need for medical supervision.
Expert Recommendations
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in determining whether phentermine and Ozempic can be used together safely. They will consider factors such as:
- The patient’s overall health and medical history
- Current medications and potential interactions
- Weight loss goals and diabetic management needs
Patients should:
- Inform their doctor of all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
- Avoid self-medicating or altering doses without medical advice.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly if diabetic.
Alternatives to Combination Therapy
For individuals who cannot safely combine these medications, there are alternative strategies for weight loss and diabetes management:
- Lifestyle Modifications: A healthy diet and regular exercise remain the cornerstone of weight management.
- Other Medications: Alternatives like liraglutide, naltrexone-bupropion, or metformin may be more suitable in some cases.
- Bariatric Surgery: In cases of severe obesity, surgical interventions may be considered.
Conclusion
The decision to combine phentermine with Ozempic should not be taken lightly. While there may be potential benefits, the risks of side effects, drug interactions, and hypoglycemia require careful medical oversight. Always consult a healthcare provider to determine the safest and most effective approach for your weight loss and diabetes management journey. Prioritizing safety and individualized care ensures the best outcomes for your health.