What Causes Acne
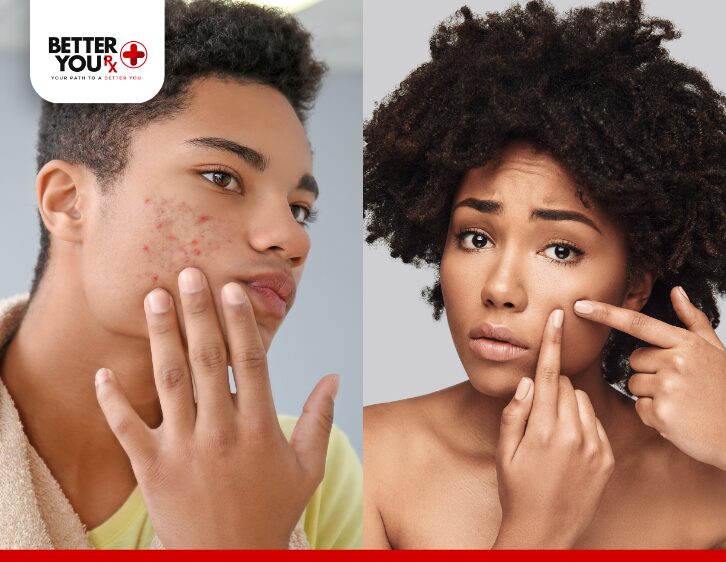
Acne remains a persistent and often frustrating skin condition, affecting both adolescents and adults. While we understand many contributing factors and the biological processes behind pimple formation, the exact cause of acne remains elusive. What we do know is that acne is influenced by a combination of variables, making it a multifactorial condition.
Understanding Acne Formation
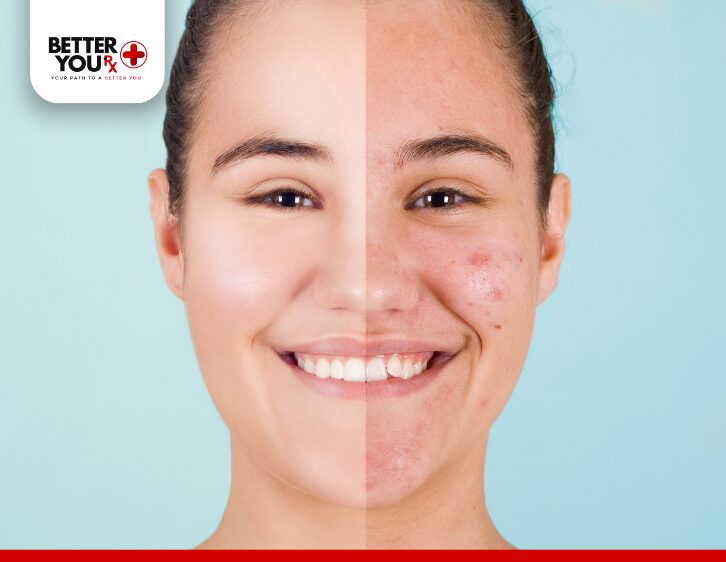

Acne develops when oil glands (sebaceous glands) near hair follicles produce excess sebum. This oil, designed to protect and lubricate the skin, can mix with dead skin cells and bacteria, leading to clogged pores. Inflammation follows, resulting in a range of skin lesions:
- Whiteheads: Pores clogged with oil and dead skin cells beneath the surface.
- Blackheads: Clogged pores exposed to air, where the oil oxidizes and darkens.
- Papules and Pustules: Inflamed bumps or pus-filled lesions on the skin.
- Cysts: Deep, painful lesions that are more severe and require medical attention.
While we know the mechanics of acne, the question remains: why do some glands clog while others don’t? The answer lies in a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Key Contributors to Acne

Research indicates that no single factor directly causes acne. Instead, a variety of elements contribute to its development:
- Hormones: Increased production of androgens during puberty, pregnancy, or hormonal changes can trigger excess sebum production.
- Inflammation: A primary driver in the formation and worsening of acne lesions.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role in susceptibility to acne.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to greasy environments or pressure/friction on the skin may exacerbate acne.
Myths vs. Facts About Acne
There are many misconceptions about what causes or worsens acne. Here are the facts:
- Diet: While greasy food doesn’t cause acne, a high-glycemic diet may contribute to flare-ups.
- Hygiene: Dirty skin isn’t the culprit. Over-scrubbing or using harsh cleansers can irritate the skin and worsen acne.
- Cosmetics: Non-comedogenic or water-based cosmetics are less likely to clog pores.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for effective acne management.
Emerging Insights: The Mind-Body Connection
New research underscores the link between stress and acne. Emotional and physical stress can affect various bodily systems, including the skin, potentially worsening acne outbreaks. This aligns with the growing recognition of the mind-body connection in dermatological conditions.
Some studies also suggest that low levels of antioxidants, such as Vitamins A and E, might play a role in acne development. Additionally, there’s evidence that inflammation itself could act as a catalyst for acne, further highlighting the importance of anti-inflammatory treatments.
Managing and Treating Acne

Effective acne treatment often requires a tailored approach, addressing the specific triggers and severity of the condition. From topical solutions to oral medications, Better You Rx offers a range of options to help manage acne and improve skin health.
Need Help?
If you have questions or are ready to order your acne medication, call 1-647-576-2076 to speak with a representative.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider regarding your condition and treatment options.