Diabetic blisters may seem like a minor inconvenience, but they can lead to significant health risks for those living with diabetes. This article aims to uncover the nature of diabetic blisters, their causes, symptoms, treatment options, prevention strategies, and much more. Gaining insight into this common complication can help you manage your health more effectively and prevent potential complications.
What Are Diabetic Blisters?
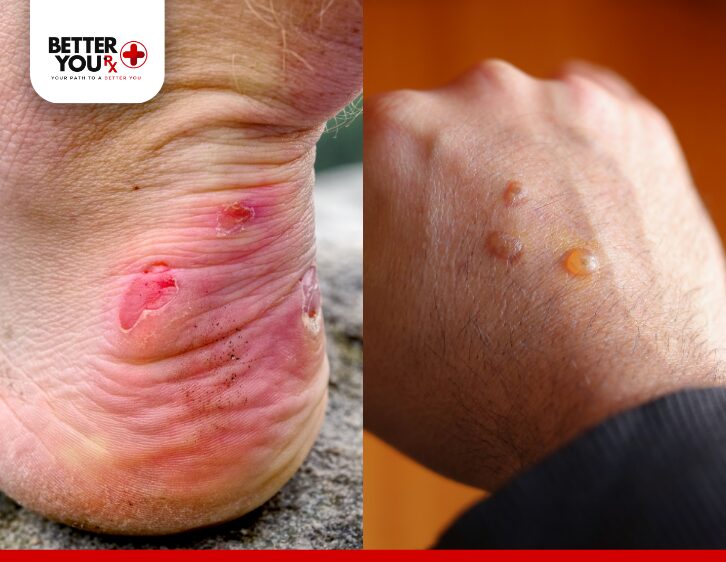
Diabetic blisters are fluid-filled sacs that appear on the skin, primarily in individuals with diabetes. They can develop suddenly, often without any preceding trauma, and are usually found on the hands, feet, and occasionally the forearms. Unlike regular blisters, which are often caused by friction or burns, diabetic blisters can occur due to underlying health conditions related to diabetes. They can range in size and typically contain clear or yellowish fluid. While many diabetic blisters are painless, they can lead to severe complications if not properly cared for, especially in those with nerve damage or poor circulation.
Causes of Diabetic Blisters
Understanding the underlying causes of diabetic blisters is crucial for prevention and management. Several factors contribute to their formation:
1. Poor Blood Sugar Control: High blood sugar levels can damage the small blood vessels in the skin, leading to skin changes that make it easier for blisters to form. Chronic hyperglycemia can also result in reduced blood flow, increasing the risk of skin injuries and blisters.
2. Nerve Damage: Diabetic neuropathy affects the nerves in the extremities, reducing sensitivity and making it difficult for individuals to feel injuries or friction. This lack of sensation can lead to unnoticed injuries that develop into blisters.
3. Injury or Friction: Even minor injuries, such as cuts, scrapes, or friction from shoes or clothing, can lead to blister formation, particularly in individuals with diabetes who may not be aware of these injuries due to neuropathy.
4. Skin Conditions: Certain dermatological conditions can predispose individuals with diabetes to blister formation. For example, conditions like bullosis diabeticorum can cause blisters to appear on the skin without any apparent reason.
By understanding these causes, individuals with diabetes can take proactive measures to prevent blister formation.
Symptoms of Diabetic Blisters
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetic blisters is essential for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Fluid-Filled Sacs: Diabetic blisters typically appear as fluid-filled sacs on the skin, which can range in size from small to large. The fluid inside is usually clear, although it may become cloudy or discolored if an infection develops.
- Surrounding Redness: The skin around the blister may appear red, swollen, or inflamed, indicating irritation or an underlying issue.
- Painlessness: One of the hallmark features of diabetic blisters is that they are often painless, particularly in individuals with nerve damage. However, if an infection occurs or if pressure is applied, they may become uncomfortable.
Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent complications, as prompt treatment is essential.
Diabetic Blisters Treatment
Effective treatment of diabetic blisters is crucial for preventing infection and promoting healing. Here are several recommended treatment options:
- Keep the Area Clean: Gently wash the blister and surrounding skin with mild soap and water to remove any dirt or bacteria. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scrubbing the area aggressively, as this can worsen irritation.
- Do Not Pop the Blister: It’s important not to pop or drain a diabetic blister, as this can increase the risk of infection. The blister acts as a protective barrier that helps the underlying skin heal.
- Apply a Bandage: Cover the blister with a sterile, non-adhesive bandage to protect it from further injury and keep it clean. Replace the bandage frequently, particularly if it becomes damp or dirty.
- Monitor for Infection: Regularly check the blister for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or the presence of pus. If any of these symptoms develop, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: If the blister does not improve, becomes painful, or if you have other underlying health issues, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.

How to Prevent Diabetic Blisters
Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to diabetic blisters. Here are some effective strategies to help prevent their formation:
- Manage Blood Sugar Levels: Keeping blood sugar levels within the target range is vital for reducing the risk of diabetic complications, including blisters. Regular monitoring and adherence to prescribed medication can help achieve stable glucose levels.
- Inspect Your Skin Daily: Conduct daily inspections of your feet and hands for any signs of blisters, cuts, or abrasions. Identifying issues early enables timely action, lowering the chances of complications.
- Wear Comfortable Shoes: Choose shoes that fit well, provide ample support, and minimize friction. Avoid tight or ill-fitting footwear that can cause pressure points, leading to blister formation.
- Moisturize: Regularly applying a moisturizer to your skin can help keep it hydrated and maintain its integrity. This practice can help prevent dryness and cracking, which may increase the risk of blister development.
Diabetic Blisters vs. Regular Blisters
While diabetic blisters may appear similar to regular blisters, there are key differences that set them apart. Regular blisters often arise from friction, burns, or other external factors and typically heal relatively quickly once the underlying cause is addressed. In contrast, diabetic blisters can occur without apparent injury and may be indicative of more serious underlying health issues. Furthermore, diabetic blisters may take longer to heal due to compromised circulation and nerve function associated with diabetes.
Are Diabetic Blisters Painful?
In most cases, diabetic blisters do not cause pain, particularly in individuals with nerve damage, as the affected areas may lack sensitivity. However, if the blister becomes infected, develops complications, or if excessive pressure is applied, it can lead to discomfort or pain. It’s important to monitor any changes and consult a healthcare professional if pain develops.
Home Remedies for Diabetic Blisters
In addition to medical treatment, some home remedies can aid in the healing process and provide relief:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, aloe vera gel can be applied directly to diabetic blisters to help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Its natural antimicrobial properties can also assist in preventing infection.
- Coconut Oil: Rich in fatty acids and known for its antimicrobial properties, coconut oil can be used to moisturize the skin and provide a protective barrier against bacteria, potentially preventing infection.
- Honey: A natural antibiotic, honey can be applied to blisters to help keep the area moist, promote healing, and prevent infection due to its antibacterial properties.
How to Care for Diabetic Blisters
Proper care is crucial for diabetic blisters to ensure effective healing and prevent complications. Here’s a comprehensive approach to caring for them:
1. Clean the Area: Use a gentle soap and water solution to clean the blister and the surrounding skin. Pat the area dry with a clean towel.
2. Apply an Antibiotic Ointment: Consider applying an over-the-counter antibiotic ointment to the blister to help prevent infection. This can provide an additional layer of protection.
3. Cover the Blister: Use a sterile, non-stick bandage or dressing to cover the blister. This will protect it from friction and dirt while allowing it to heal.
4. Change the Dressing Regularly: Keep the area clean and dry by changing the bandage daily or whenever it becomes wet or soiled. This helps maintain a healthy environment for healing.
5. Avoid Pressure and Friction: Try to minimize pressure on the blistered area. If the blister is on your foot, avoid walking long distances or wearing tight shoes until it heals.

When to See a Doctor for Diabetic Blisters
It’s important to seek medical attention if you notice any of the following signs:
- Signs of Infection: If you observe increased redness, swelling, warmth, or the presence of pus, these may indicate an infection that requires medical intervention.
- Persistent or Painful Blisters: If the blister is large, painful, or does not show signs of healing after a few days, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
- Underlying Health Issues: If you have additional health concerns, such as peripheral artery disease or other conditions that may complicate healing, it’s best to seek medical advice.
Conclusion
Diabetic blisters may appear harmless, but they can lead to significant complications if not addressed properly. By understanding their causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective treatment strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing these blisters. Mounjaro serves as an innovative treatment option for managing diabetes, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications such as diabetic blisters.
If you’re looking for accessible and affordable medications, consider Better You Rx. This online Canadian Pharmacy Affiliate referral service offers a range of cheap drugs and meds from Canada, including essential diabetes treatments. With options for cheap medicines and convenient access to medications online, Better You Rx is dedicated to supporting your health journey. Prioritize your well-being and take the necessary steps to manage your diabetes effectively with Mounjaro and the resources available through Better You Rx.