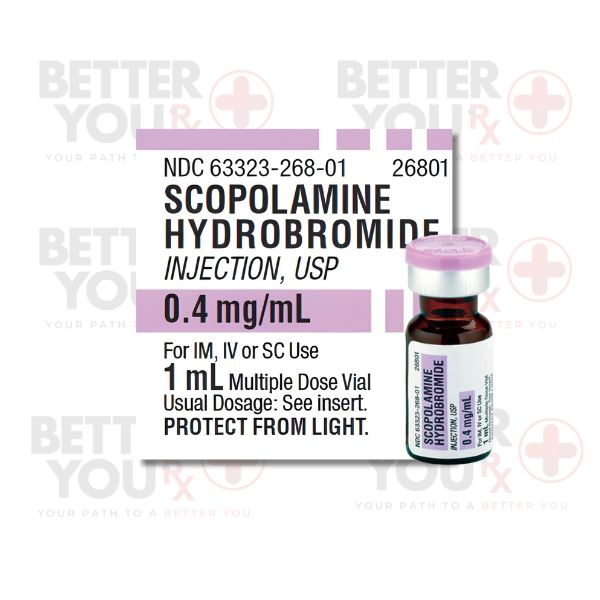
Indications:
● Prophylaxis of nausea and vomiting related to motion sickness.
● Prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) after anesthesia and surgery.
● Adjunct therapy for gastrointestinal cramping.
Administration Guidelines:
● Scopolamine is available in transdermal patches applied to the skin behind the ear for extended release over several days, typically formulated as 1.5 mg for motion sickness.
● Patches should be applied several hours before the desired antiemetic effect can last up to 3 days.
● If used for surgery, it is generally applied the evening before the procedure.
Dosage Forms:
● Transdermal patches are the most common form, but Scopolamine can also be administered via injection or as an oral tablet in different dosages.
Safety Preclusions
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
● Scopolamine should be used during pregnancy only if needed and after assessing the risks and benefits. It is not known if Scopolamine is excreted in breast milk; caution is advised.
Long-term Use:
● Long-term use of Scopolamine is generally not recommended because of its potential side effects and the typically episodic requirement for its antiemetic effects.
Drug Interactions:
● Scopolamine may have additive effects when used with other anticholinergic drugs, sedatives, or alcohol. Caution is advised when combining medications with similar effects or with medications that are metabolized by similar pathways
|



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.