Diabetes and heart disease are two of the most prevalent chronic conditions in the world today, and they often occur together. The relationship between diabetes and heart disease is complex but deeply intertwined. In this article, we will explore how diabetes can contribute to the development of heart disease, the risk factors involved, and the steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of both conditions.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition that occurs when the body is unable to properly process blood sugar (glucose). It affects the way the body converts food into energy. There are two main types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes must take insulin regularly to help manage their blood glucose levels.
- Type 2 Diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas fails to produce sufficient insulin.It is more common than type 1 diabetes and is often related to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and being overweight.
Both types of diabetes can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which, over time, can cause damage to the body’s organs and tissues. Among the most significant risks is heart disease, which is common among individuals with diabetes.
What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease, or cardiovascular disease (CVD), is an umbrella term used to describe a range of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. TDiabetes-related complications often involve cardiovascular issues, such as coronary artery disease (which can trigger heart attacks), heart failure, arrhythmias, and peripheral artery disease. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and the heart over time, making individuals with diabetes more susceptible to developing heart disease.
How Diabetes Increases the Risk of Heart Disease
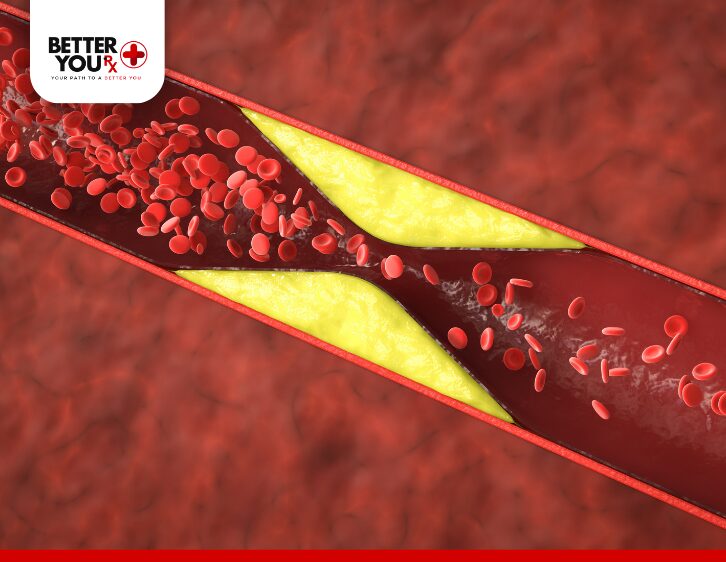
There are several ways in which diabetes can contribute to the development of heart disease. Elevated blood sugar levels can have a negative impact on blood vessels, heart function, and overall cardiovascular health.
1. Damage to Blood Vessels
Chronic high blood sugar levels in diabetes lead to a condition known as atherosclerosis, or the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. Over time, these deposits can harden and narrow the arteries, making it more difficult for blood to flow through them. As a result, the risk of experiencing heart attacks and strokes is significantly heightened.
2. High Blood Pressure
People with diabetes are more likely to have high blood pressure, or hypertension, which can further damage the blood vessels. The combination of high blood sugar and high blood pressure significantly raises the risk of heart disease.
3. Increased Cholesterol Levels
Diabetes, especially when poorly managed, can lead to an imbalance in cholesterol levels. Specifically, it often results in higher levels of bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglycerides, both of which contribute to the formation of plaque in the arteries. On the other hand, good cholesterol (HDL) may be lower in individuals with diabetes, which is important for removing harmful cholesterol from the bloodstream.
4. Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is common in individuals with diabetes, which can contribute to the development of heart disease. Inflammation damages the blood vessels, making it easier for plaque to form and disrupt normal blood flow.
5. Obesity and Insulin Resistance
Being overweight or obese is a key risk factor for both diabetes and heart disease. Obesity leads to insulin resistance, which in turn causes blood sugar levels to rise. Insulin resistance also contributes to increased fat accumulation around the heart and blood vessels, exacerbating heart disease risk.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease Among People with Diabetes
While the direct relationship between diabetes and heart disease is concerning, there are several factors that further increase the risk of heart disease for individuals with diabetes. These include:
- Age: As people with diabetes get older, their risk of heart disease increases.
- Gender: Men with diabetes have a higher risk of heart disease than women, but women with diabetes also face a heightened risk, especially after menopause.
- Family history: A family history of heart disease or diabetes can increase the likelihood of developing heart disease.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels, and when combined with diabetes, it amplifies the risk of heart disease.
- Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of both developing diabetes and experiencing cardiovascular problems.
- Poor diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and fats can increase the risk of both conditions.
Symptoms of Heart Disease in People with Diabetes

Individuals with diabetes may not experience any symptoms of heart disease until the condition becomes severe. However, some warning signs may include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
It is important for people with diabetes to monitor their heart health regularly and seek medical attention if any of these symptoms arise.
Preventing Heart Disease for People with Diabetes

Although the risk of heart disease is higher for individuals with diabetes, there are steps that can be taken to reduce that risk. Effective management of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining heart health.
1. Control Blood Sugar Levels
Proper blood sugar management is the foundation of effective diabetes care. These benefits can be achieved through a combination of medication, lifestyle adjustments, and consistent monitoring of glucose levels. Regularly testing blood sugar and working with a healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan can help keep levels in check.
2. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A healthy diet is crucial for managing both diabetes and heart disease. A nutritious diet that emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Reducing intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and processed foods can help manage cholesterol levels and promote heart health.
3. Exercise Regularly
Regular physical activity supports blood glucose control and significantly lowers the risk of heart disease. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or swimming. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve cardiovascular health.
4. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Reaching and maintaining a healthy weight is vital for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Even modest weight loss can decrease insulin resistance and enhance blood sugar regulation. It also helps lower the risk of high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
5. Quit Smoking
Smoking significantly increases the risk of heart disease, especially in people with diabetes. Quitting smoking improves circulation, reduces blood pressure, and decreases the risk of complications such as heart attack and stroke.
6. Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Levels
Regularly checking blood pressure and cholesterol levels is important for people with diabetes. If either is high, working with a healthcare provider to manage these conditions can help reduce the risk of heart disease. Medications, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both may be necessary.
7. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to high blood sugar and increase the risk of heart disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or mindfulness can be helpful in managing both diabetes and heart health.
Conclusion
The link between diabetes and heart disease is undeniable, and the risk of developing cardiovascular problems is significantly higher for individuals with diabetes. However, with careful management of blood sugar, regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and routine monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels, the risk of heart disease can be greatly reduced. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can improve their overall health and quality of life.
If you or a loved one has diabetes, it’s crucial to stay vigilant about heart health. Regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications can help prevent heart disease and allow individuals to lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.



