What is the Best Time of Day to Take Basaglar?
Managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment that involves careful attention to lifestyle, diet, and medication. One such medication commonly used to manage blood sugar levels is Basaglar, an insulin glargine product. Basaglar is a long-acting insulin that helps control blood sugar by releasing a steady amount of insulin over an extended period. It is typically injected once a day, but many individuals wonder when the best time is to take it for optimal effectiveness.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the best time of day to take Basaglar, the factors that influence this decision, and how to properly integrate it into your daily routine. Whether you’re new to Basaglar or looking for tips on optimizing your insulin regimen, this article offers valuable insights to help you make the most of your treatment plan.
Understanding Basaglar: What It Is and How It Works
Before diving into the specifics of when to take Basaglar, it’s essential to understand what the medication does. Basaglar is a long-acting insulin that helps lower blood sugar levels in individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Insulin glargine, the active ingredient, mimics the body’s natural insulin by providing a continuous, slow release of insulin. This helps manage glucose levels, particularly during fasting periods, such as overnight.
Unlike rapid-acting insulin, which works quickly after injection, Basaglar maintains a steady blood sugar level throughout the day. Typically, Basaglar is injected once daily, and your doctor will determine the right dose based on factors like body weight, diet, and other health conditions.
Why the Timing of Your Basaglar Dose Matters
The timing of insulin injections plays a crucial role in how well the medication works. Since Basaglar is a long-acting insulin, its effectiveness is not influenced by meal times or immediate spikes in blood sugar, unlike rapid-acting insulins. However, consistent timing of your dose can help maintain steady blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
While some people may not notice a difference in their blood sugar levels regardless of when they take their dose, for many, sticking to a specific time each day can improve the medication’s overall effectiveness. The key is establishing a routine that works for your lifestyle while ensuring that Basaglar continues to meet your blood sugar management goals.
Best Time of Day to Take Basaglar: Morning or Evening?
The best time of day to take Basaglar can depend on several factors, including your personal schedule, blood sugar patterns, and the advice of your healthcare provider. However, many individuals choose either morning or evening for their injection. Let’s take a look at the pros and cons of each time:
Morning Doses of Basaglar
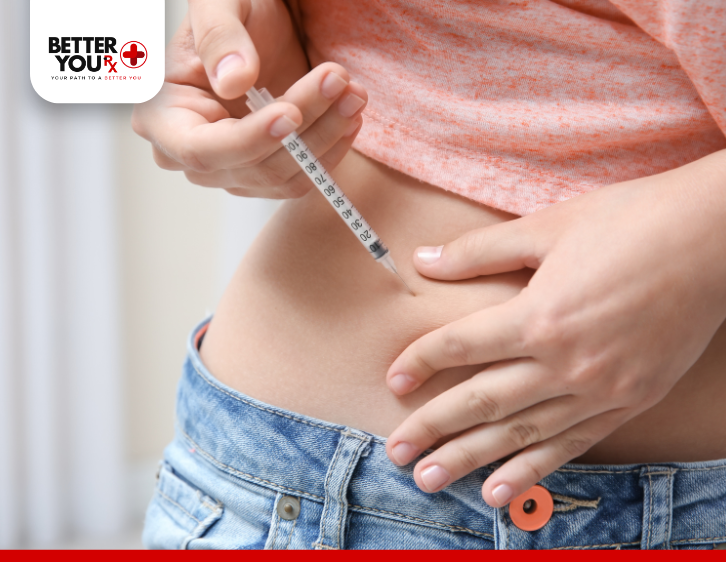

Taking Basaglar in the morning is ideal for individuals who have a consistent routine and are able to inject their dose at the same time each day. For some, this might feel more convenient, as it can be done right after waking up, before starting daily activities.
Pros of Taking Basaglar in the Morning:
- Easier to Remember: Injecting at the same time each morning helps build a routine.
- Steady Blood Sugar Control Throughout the Day: Since Basaglar lasts for about 24 hours, starting in the morning ensures that the medication works throughout the day.
- Fit with Routine: Many people find it easier to incorporate insulin injections into their morning habits, like brushing teeth or eating breakfast.
Cons of Morning Doses:
- Blood Sugar Spikes in the Morning: Some individuals experience “dawn phenomenon,” where blood sugar levels rise early in the morning. In such cases, Basaglar alone may not be enough to control these fluctuations, and additional medications or adjustments may be necessary.
Evening Doses of Basaglar
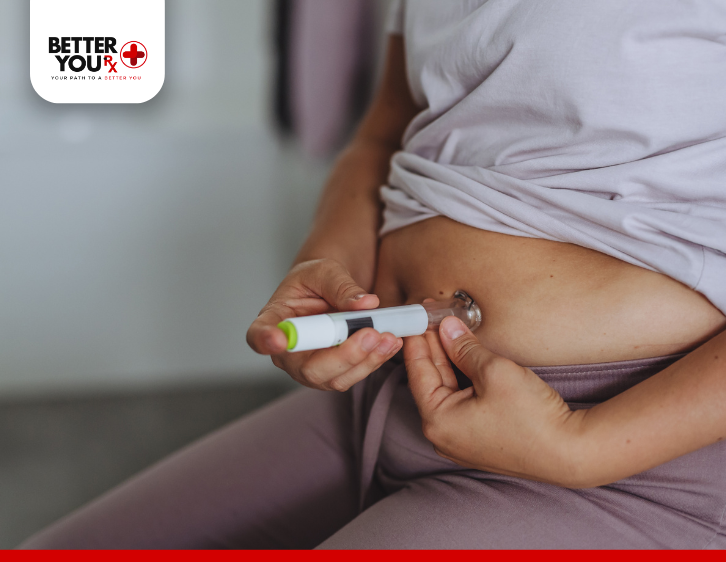

For some individuals, injecting Basaglar in the evening may be more practical. This is especially true for people who experience higher blood sugar levels in the morning or are looking for more consistent control throughout the night.
Pros of Taking Basaglar in the Evening:
- Overnight Blood Sugar Control: Basaglar’s gradual release helps keep blood sugar steady overnight, reducing the likelihood of high morning glucose levels.
- Fits Better with Busy Mornings: Evening doses may be preferable for those who find mornings rushed or who forget their injection.
- Improved Blood Sugar Regulation: For some, the evening dose ensures that blood sugar is balanced through the night, helping avoid spikes in the morning.
Cons of Evening Doses:
- Harder to Track in the Morning: If you need to adjust your insulin dose based on your morning blood sugar reading, taking your dose at night might make it more challenging to monitor.
- Sleep Disruptions: For some individuals, injections before bed can interfere with sleep, particularly if they are experiencing side effects like hypoglycemia.
Factors Influencing the Timing of Your Basaglar Dose
While many people benefit from injecting Basaglar at the same time each day, the optimal time for you will depend on several factors:
- Blood Sugar Patterns: If you experience blood sugar spikes in the morning (dawn phenomenon), taking Basaglar in the evening may help. If your blood sugar is higher in the evening, a morning dose could be more effective.
- Your Daily Routine: Consider your lifestyle. If mornings are chaotic or you prefer to inject your dose before bed, choose a time that aligns with your daily routine.
- Diet and Exercise: Diet and physical activity levels can also affect how your body responds to Basaglar. Adjustments to your insulin timing may be necessary if these factors change.
- Consistency is Key: The most important factor is consistency. Taking your Basaglar at the same time every day, whether it’s in the morning or evening, ensures that your insulin levels remain stable throughout the day.
- Healthcare Provider’s Advice: Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your insulin regimen. They can help you determine the best time to take Basaglar based on your specific needs and health conditions.
How to Inject Basaglar: Best Practices
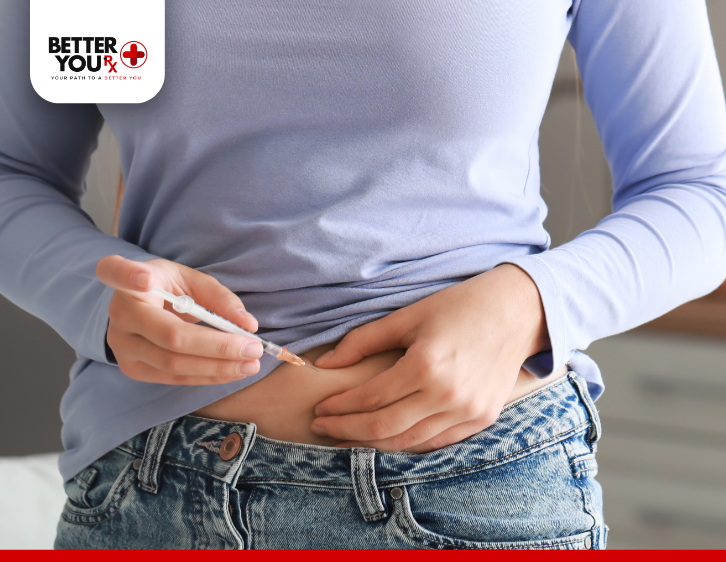

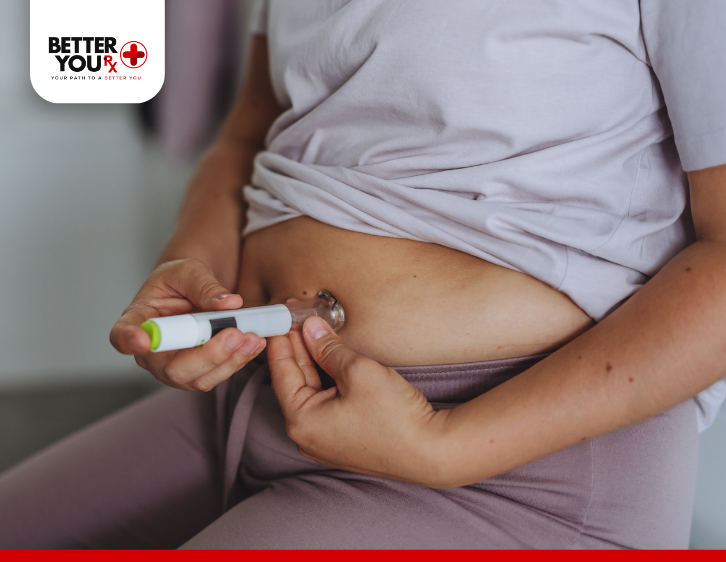
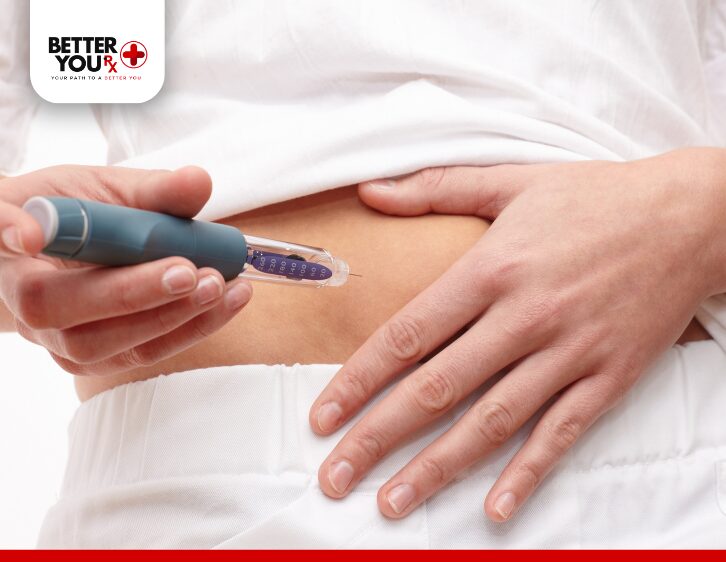
For those who have been prescribed Basaglar, it’s crucial to follow proper injection techniques to ensure that the medication works as intended. Basaglar is administered subcutaneously (under the skin) using either the KwikPen or Tempo Pen, both of which come pre-filled with insulin.
Injection Sites:
- Stomach (abdomen): This is typically the most preferred site for insulin injections as it allows for better absorption.
- Thighs and Upper Arms: These areas can also be used but may lead to slightly slower absorption.
Rotation of Injection Sites: It’s important to rotate the injection sites to avoid irritation or lumps under the skin. Stick to one area for a period of time (e.g., abdomen) before switching to another (e.g., thighs).
Storage: Store Basaglar in a refrigerator until it is ready for use. Once opened, it can be stored at room temperature for up to 28 days.
Adjusting Your Basaglar Dosage
As with any medication, you may need adjustments to your Basaglar dosage over time. Your healthcare provider will monitor your blood sugar levels and may recommend changes based on your blood sugar readings, weight changes, or new health conditions.
Always keep your healthcare provider informed about any changes to your diet, exercise habits, or other medications you are taking. These factors can impact how well Basaglar works and whether your dosage needs to be adjusted.
Conclusion: Establishing Your Basaglar Routine
Determining the best time of day to take Basaglar ultimately depends on your personal schedule, your body’s response to the medication, and your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Whether you choose to inject in the morning or evening, the key to success lies in consistency and monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly.
If you are interested in learning more about Basaglar or need help with your insulin regimen, reach out to a healthcare professional. And remember, subtle adjustments may be needed over time, so keep in close contact with your doctor to ensure you’re managing your diabetes effectively.