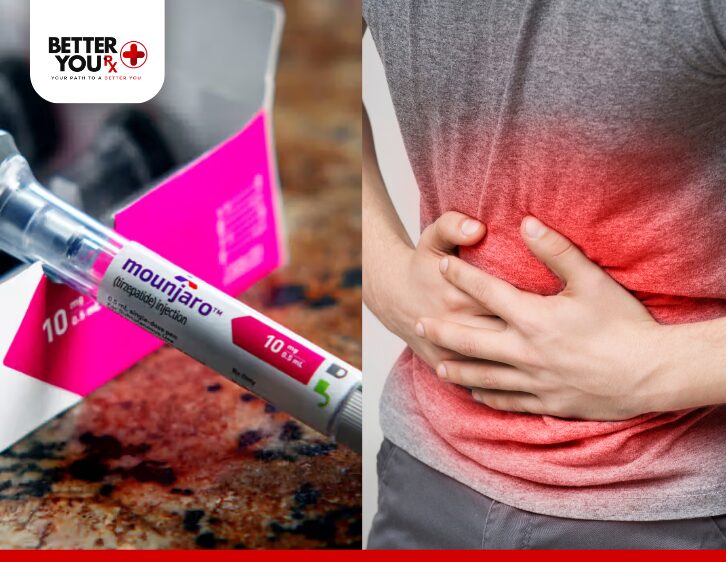
Does Mounjaro Cause Constipation?
Mounjaro (tirzepatide) is a relatively new medication that has gained attention for its effectiveness in managing type 2 diabetes and aiding in weight loss. It works by stimulating insulin secretion, reducing appetite, and enhancing glucose control. While many patients have experienced positive outcomes from Mounjaro, like improved blood sugar levels and weight loss, it is not without potential side effects. One of the most commonly reported issues by users is gastrointestinal discomfort, including constipation. This leads many people to wonder: does Mounjaro cause constipation?
In this article, we’ll explore the connection between Mounjaro and constipation, how the medication affects the digestive system, and what patients can do to alleviate this side effect.
Understanding Mounjaro and How It Works
Mounjaro is part of a group of drugs called GLP-1 receptor agonists, which mimic the effects of glucagon-like peptide-1. It is also a GIP (gastric inhibitory peptide) receptor agonist, making it a dual-agonist drug. This dual action helps to regulate insulin secretion after meals, reduce appetite, slow gastric emptying, and improve blood sugar levels. It is administered through a weekly injection and has shown to be highly effective in managing blood sugar and promoting weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes.
While Mounjaro offers many benefits, its effect on the digestive system is one of the key concerns for patients. Slower gastric emptying, one of the medication’s mechanisms of action, can cause food to remain in the stomach for longer periods, which may lead to discomfort and changes in bowel movements, such as constipation.
How Mounjaro May Cause Constipation

Constipation is a well-documented side effect of Mounjaro, particularly in the early stages of treatment. This is largely due to its ability to slow down gastric motility — the movement of food through the stomach and intestines. As a result, food takes longer to digest and pass through the digestive system. This slowed digestion can lead to a buildup of stool in the intestines, resulting in constipation.
Another contributing factor is Mounjaro’s impact on appetite. Many people using Mounjaro experience a significant reduction in appetite, which may lead to eating smaller meals or irregular meal times. Inadequate food intake or changes in diet can disrupt normal bowel function and contribute to constipation.
Additionally, like other GLP-1 receptor agonists, Mounjaro can affect the function of the colon. The colon functions to absorb excess water from stool and guide its passage to the rectum for proper elimination. Slower gastric emptying can result in more water being absorbed from the stool, making it harder and more difficult to pass.
Symptoms of Constipation Caused by Mounjaro
Patients taking Mounjaro may experience a variety of symptoms related to constipation. These can include:
- Difficulty passing stool
- Infrequent bowel movements (fewer than three per week)
- Hard, dry stools
- Abdominal bloating or discomfort
- Feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation
- Cramping or stomach pain
Some individuals may experience mild constipation, while others may have more severe symptoms. In some cases, constipation can be accompanied by other gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea or vomiting, which can also be side effects of Mounjaro.
How Common Is Constipation with Mounjaro?
Constipation is a known side effect of Mounjaro, but not all patients will experience it. According to clinical studies and patient reports, gastrointestinal side effects like constipation, nausea, and diarrhea are among the most common complaints, but they tend to improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication. In clinical trials, about 20% to 30% of patients reported experiencing gastrointestinal side effects, including constipation, when using Mounjaro.
The severity of constipation can vary based on individual factors, such as diet, lifestyle, and the presence of other health conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or a history of constipation. It is also important to note that the dose of Mounjaro can affect the likelihood and severity of constipation. Higher doses may be more likely to cause gastrointestinal issues, including constipation, as the body adjusts to the medication.
How to Manage Constipation While Taking Mounjaro

If you are experiencing constipation while taking Mounjaro, there are several strategies you can try to alleviate this uncomfortable side effect. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your routine or treatment plan.
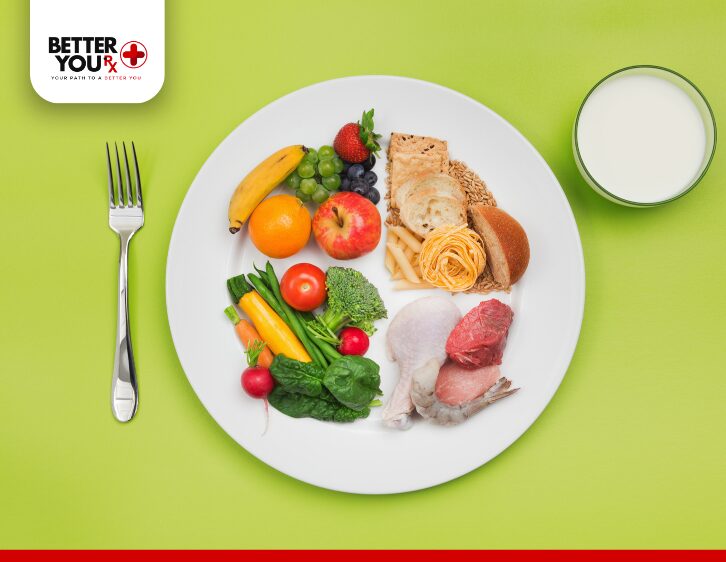
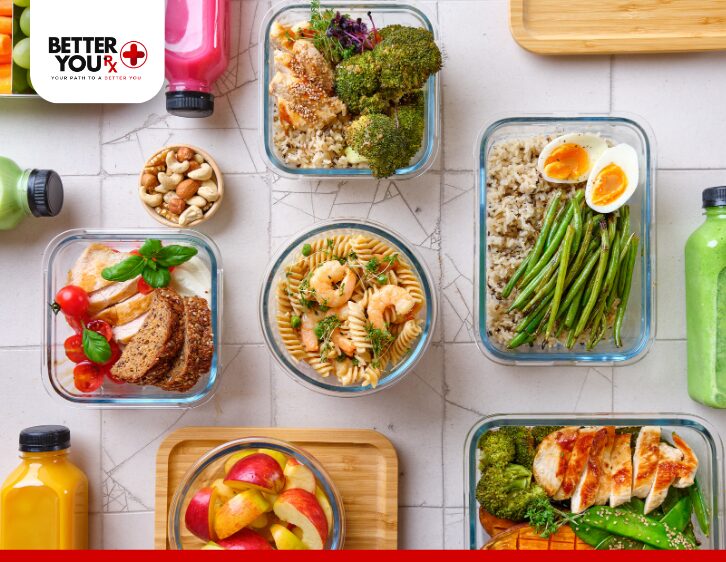
- Boosting your fiber intake is a highly effective strategy for preventing or relieving constipation through diet. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help promote regular bowel movements and soften the stool. Fiber increases stool volume, which encourages regular bowel movements and helps alleviate constipation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is crucial when managing constipation. Staying hydrated softens the stool, which supports smoother elimination. Try to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, and increase your intake if you’re engaging in physical activity.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity helps stimulate the muscles in the intestines, promoting regular bowel movements. Simple activities like walking can effectively support digestive health and reduce the risk of constipation.
- Consider Laxatives: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend a mild over-the-counter laxative to help relieve constipation. Laxatives should be used only as a short-term solution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid dependency.
- Adjust Mounjaro Dosage: If constipation becomes severe or persistent, it’s important to discuss this with your doctor. They may recommend adjusting the dosage of Mounjaro or switching to a different medication to minimize gastrointestinal side effects.
- Probiotics: Some patients find relief from constipation by incorporating probiotics into their diet. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help support gut health and promote regular bowel movements.
When to Contact Your Healthcare Provider

While mild constipation may be manageable with lifestyle changes, it’s important to reach out to your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent constipation that doesn’t improve with diet or hydration changes
- Abdominal pain or bloating that worsens over time
- Vomiting or nausea in addition to constipation
- A sudden change in bowel habits that lasts more than a few days
These could be signs of a more serious issue, such as an obstruction in the bowel or other gastrointestinal concerns, which would require medical attention.
Conclusion
Constipation is a common side effect of Mounjaro, especially in the early stages of treatment. The medication’s ability to slow gastric emptying and reduce appetite can lead to digestive disruptions, including constipation. However, this side effect is usually temporary and can be managed with dietary adjustments, hydration, exercise, and other strategies. If constipation becomes severe or persistent, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan.
By understanding the link between Mounjaro and constipation and knowing how to manage this side effect, patients can continue to benefit from the medication’s positive effects on blood sugar and weight management while maintaining digestive health.

























 Diabetes
Diabetes






