Eliquis: A lifesaver for many, but a puzzle for some. This blood-thinning medication comes in 5mg and 2.5mg tablets. But what if your doctor prescribes a lower dose? Can you simply cut a 5mg tablet in half?
The short answer: It’s complicated.

While technically possible, splitting Eliquis carries risks. Irregular amounts disrupt this sensitive medicine, causing severe repercussions.
We’ll explore these points and share expert insights. They will help you make informed health decisions.
Eliquis, a crucial medication for preventing blood clots, often comes in 5mg tablets. But what if your doctor prescribes a lower dose? The temptation to simply cut a tablet in half can be strong. However, as with most things in healthcare, it’s not that simple.
The Perils of DIY Dosage
While it might seem harmless, splitting Eliquis carries significant risks:
- Uneven doses: There’s no guarantee that you’ll cut the tablet perfectly in half, leading to inconsistent medication levels in your body.
- Increased risk of blood clots or bleeding: Too little Eliquis can increase the risk of blood clots, while too much can lead to excessive bleeding.
Eliquis (apixaban) is a common blood thinner. It treats and prevents blood clots. It comes in 5 mg and 2.5 mg tablets. Doctors prescribe lower 2.5 mg doses to some patients. This raises questions about splitting the 5 mg tablets in half.
This article covers all about splitting Eliquis. It includes the risks, proper technique, safety measures, and expert opinions. Eliquis tablets are “splittable.” But patients must take precautions for safe use. Consult your healthcare provider. They will tell you if you can split tablets.
What is Eliquis and How is it Used?

Eliquis is the brand name for the drug apixaban, which belongs to a class of anticoagulants known as factor Xa inhibitors. It works by blocking factor Xa, a protein involved in blood clot formation.
Eliquis is Drug Administration-approved for:
- Preventing blood clots in patients who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery. The usual dose is 2.5 mg taken twice daily.
- Treating and preventing recurrence of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). The dose varies between 10 mg twice daily, 5 mg twice daily, and 2.5 mg twice daily depending on the condition.
- Preventing stroke and blood clots in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The usual dose is 5 mg twice daily.
Eliquis comes in round, yellow, film-coated tablets in 5 mg and 2.5 mg strengths. The tablets are NOT scored, meaning there is no line down the middle to guide breaking them in half.
People often split pills to save money or to swallow them more easily. This is especially true for older adults and those with dysphagia, a swallowing difficulty. As a geriatric pharmacist, I frequently encounter this scenario. It may seem harmless to cut Eliquis (apixaban) in half. But, it is crucial to do so with precision. Uneven dosing can significantly impact its effectiveness. This article examines Eliquis tablets, U.S. Regulatory Standards, and the risks of splitting the drug.
Can You Cut Eliquis in Half?
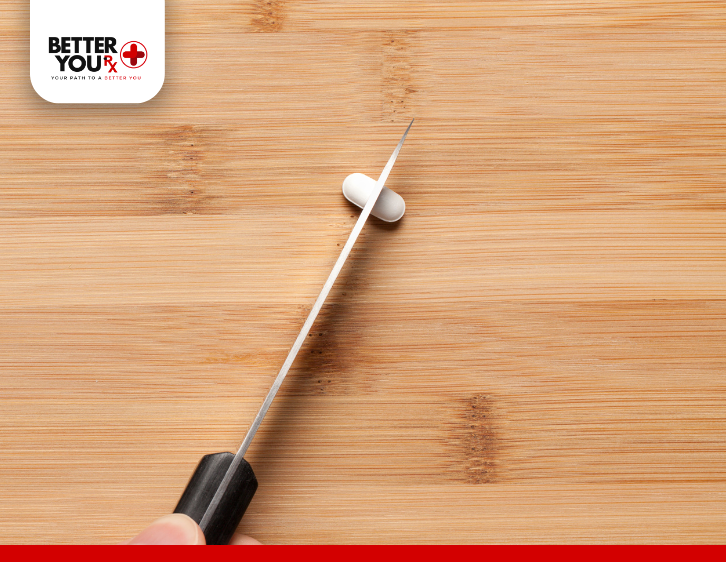
Yes, it is possible to cut Eliquis in half, but it must be done accurately to avoid uneven dosing. Here’s a brief overview of what you need to know before we explore the details.
The Formulation of Eliquis Tablets
Eliquis tablets are film-coated to protect the drug from humidity and heat and to mask its bitter taste. This coating aids in absorption and keeps the medicine effective. Cutting the tablet will damage the film coating. But, it won’t affect the drug’s efficacy. But, improper splitting can cause an uneven distribution of the active ingredient. This may reduce effectiveness or cause side effects.
The tablets have active and inactive ingredients. Their uniformity is crucial for consistent dosing. Improper splitting can disrupt the uniformity of the medication. This may lead to inaccurate dosing. It could reduce the drug’s effectiveness and increase side effects.
Regulations and Guidelines
The Drug Administration regulates medication safety and effectiveness, including tablet splitting. While some tablets are scored to facilitate splitting, Eliquis tablets are not. The Drug Administration does not recommend or endorse splitting Eliquis tablets, though it is technically feasible. So, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider before changing how you take this medication.
Scored tablets are to be split along a marked line. This ensures each half has an equal amount of the medication. Eliquis tablets are not scored. So, splitting them is hard. This may cause inconsistent dosing.
How Do You Know if You Can Cut Eliquis in Half?

In general, tablets that are scored can be split safely, but this does not apply to all medications. Do not split extended-release formulations. It may change their release mechanism. For example, metoprolol succinate and Sinemet CR must be taken whole. This ensures their timed release. Eliquis, being a non-scored tablet, falls into a different category.
For accurate info on splitting a medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist. The medication’s package insert often provides guidance on whether it can be cut. If the insert does not specify, seeking professional advice is crucial.
Risks and Precautions of Splitting Pills
Splitting pills carries inherent risks. Improper splitting can lead to inaccurate dosing, either under-dosing or overdosing. This can compromise the effectiveness of the medication and increase the risk of adverse effects. Studies show that about 1 in 8 split pills have dosing errors over 20%. This can greatly affect treatment outcomes.
Given its role in preventing blood clots and strokes, the risks of improper dosing of Eliquis are concerning. Inconsistent dosing can lead to either an increased risk of clotting events or excessive bleeding.
How to Split a Pill in Half
If you need to split a pill, follow these guidelines to ensure accuracy:
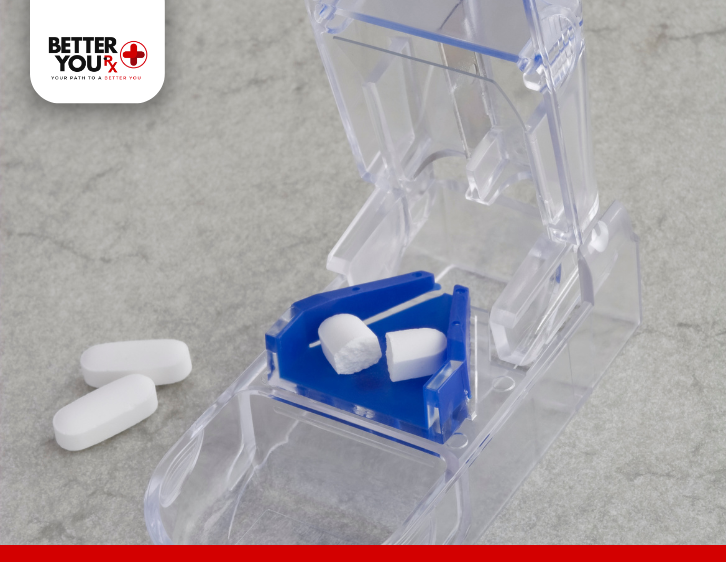
- Use a Specialized Pill Cutter: A pill cutter is designed to make clean and even cuts, reducing the risk of uneven halves.
- Press Down Quickly: Apply firm pressure quickly to avoid crumbling the pill, which can lead to uneven pieces.
- Cut One Pill at a Time: Cut only one pill at a time to prevent degradation of the medication due to exposure to moisture and heat.
- Use Clean Hands: Ensure your hands are clean to prevent contamination of the medication.
- Avoid Using Inappropriate Tools: Do not use knives, teeth, or nails to split pills. Always use a proper pill cutter to ensure a clean cut.
- Check with a Doctor or Pharmacist: Before splitting any medication, confirm with a healthcare professional that it is safe.
Why Split Eliquis Tablets?
There are several reasons why someone might consider splitting Eliquis tablets:
- Cost Savings: Cutting higher-dose tablets can help reduce the cost of medication if prescribed at a lower dose.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Smaller pieces may be easier to swallow for those who struggle with whole pills.
- Dose Adjustments: A provider may recommend splitting tablets for transitional dosing or adjusting the dose based on clinical needs.
Can Eliquis Be Crushed?
Yes, Eliquis can be crushed and mixed with water, D5W, or apple juice. It must be taken within four hours of preparation. Do not store the crushed medication for later use, as this can affect its efficacy and safety.
Crushing tablets can expose the active ingredient to the environment. This may affect the medication’s effectiveness. So, it should be done carefully.
Expert Opinions on Splitting Eliquis
Experts suggest that while splitting Eliquis tablets is possible, it should be done with caution:
- Use a Sharp Cutter: To ensure that the split tablets are as even as possible, use a high-quality pill cutter.
- Take Immediately: After splitting, consume the medication right away to avoid degradation.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Always talk to your doctor or pharmacist before changing how you take Eliquis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a pill cutter to split Eliquis?
Yes, a pill cutter or a sharp knife is recommended for making a clean split. Ensure that the pill cutter is in good condition to avoid uneven cutting.
How should I store the leftover half of the split Eliquis tablet?
Store the leftover half in the original bottle with the desiccant packet to keep it dry. Ensure the bottle is tightly sealed. Discard any unused split tablets after 24 hours to prevent exposure to moisture and degradation.
Is it safe to swallow a split Eliquis tablet?
Yes, it is generally safe to swallow split Eliquis tablets. Do not chew or crush them; swallow them whole.
Can I dissolve a split Eliquis tablet in water or juice?
No, once split, the halves should be swallowed whole. Dissolving them in water or juice is not recommended as it can affect the medication’s effectiveness.
Will cutting Eliquis tablets affect how the drug works?
If the tablet is split properly and the dose remains accurate, the medication should remain effective. Improper splitting may lead to uneven doses, which can compromise the medication’s efficacy.
Side Effects of Eliquis 5mg Twice a Day

The standard dose of Eliquis 5mg twice daily is effective for many patients, but side effects can occur. Common side effects include bleeding complications such as nosebleeds, gum bleeding, or bruising. More severe side effects may involve gastrointestinal bleeding or bleeding in the brain. It is essential to report any unusual bleeding or bruising to your healthcare provider immediately.
Eliquis Half Dose Side Effects
When Eliquis is split and taken as a half dose, maintaining therapeutic efficacy is crucial. Low doses may not prevent blood clots. This raises the risk of stroke and other complications. Check with your healthcare provider. Make sure that splitting the dose won’t harm your treatment plan.
Eliquis Side Effects in the Elderly
Elderly patients are at a higher risk for side effects from Eliquis, such as bleeding complications and kidney issues. Dosing for elderly patients often requires adjustments. This is due to kidney function and other health factors. Regular monitoring and consulting a healthcare provider are vital for managing risks.
Cutting 5mg Eliquis in Half
Cutting a 5mg Eliquis tablet in half may be necessary for dose adjustments. However, it is important to perform the cutting carefully to ensure accurate dosing. Use a pill cutter for a clean split. Check with your healthcare provider that this is suitable for your treatment.
Can Eliquis Cause Vision Problems?
Eliquis side effects rarely include vision problems. If you have vision problems while on the medication, consult your provider. They will rule out serious issues.
Eliquis 2.5 mg Criteria
The 2.5 mg dose of Eliquis is often prescribed for atrial fibrillation and a history of stroke or TIA. Criteria for prescribing this lower dose include age, kidney function, and weight. Always follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for dosage and monitoring. This ensures effective treatment.
Managing Eliquis Tablet Splitting
Splitting Eliquis tablets might seem like an easy solution for dose adjustments, but it comes with risks. Eliquis, available in 5 mg and 2.5 mg doses, is not designed to be split due to its non-scored nature. Inaccurate splitting can result in inconsistent dosing, potentially leading to ineffective treatment or increased risk of bleeding or clotting complications.
To ensure safety, use a dedicated pill cutter and consult with your healthcare provider before altering your medication routine. Proper storage and timely use of split tablets are also essential to maintain their effectiveness.
As we advance anticoagulant treatments, personalized care from healthcare providers is crucial. Each patient has unique medical needs and treatment goals. For comprehensive support and a variety of pharmaceutical options, Better You Rx is here to help. Visit our website to explore your choices and access the resources needed for effective health management.