Discover the Complexities of Type 4 Diabetes and How to Manage It Effectively
Type 4 Diabetes represents a significant advancement in our understanding of diabetes, intertwining insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and the pivotal role of cognitive function. While traditional classifications focus primarily on Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes, the emergence of Type 4 Diabetes introduces unique challenges and management strategies essential for those affected. This article delves into the characteristics, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Type 4 Diabetes, while providing actionable insights into effective lifestyle changes that can enhance overall well-being.
Understanding Type 4 Diabetes
Type 4 Diabetes, a relatively new classification, is characterized by the body’s inability to utilize insulin effectively, often resulting in insulin resistance. What sets Type 4 apart is its close association with cognitive impairments, which can influence how the brain regulates metabolic processes. This intricate relationship underscores the complexity of Type 4 Diabetes, necessitating a multifaceted approach to management that encompasses not only the physiological aspects but also cognitive functions that impact blood sugar regulation.
Symptoms of Type 4 Diabetes
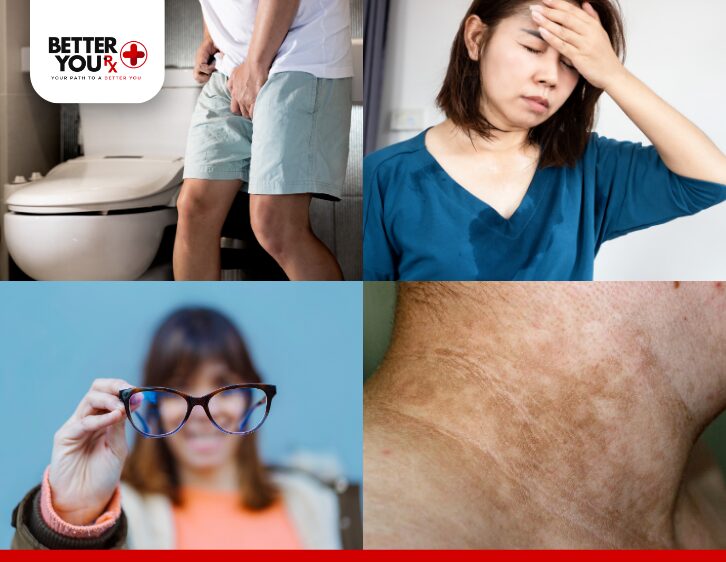
Individuals diagnosed with Type 4 Diabetes may experience a spectrum of symptoms that can significantly affect their quality of life. Identifying these symptoms is essential for prompt intervention and efficient management. Common symptoms include:
- Increased Thirst and Frequent Urination: Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to dehydration, prompting the body to signal thirst and resulting in increased urination as it attempts to eliminate excess glucose.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Insulin resistance hampers the body’s ability to convert glucose into energy, leading to persistent feelings of fatigue and weakness, often debilitating for daily activities.
- Blurred Vision: High glucose levels can distort the lenses of the eyes, causing temporary vision disturbances that can affect both near and distance sight.
- Slow-Healing Sores or Frequent Infections: Impaired circulation and elevated blood sugar can hinder the body’s healing processes, resulting in wounds that take longer to heal and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Darkened Skin Areas: Individuals may notice patches of darkened skin, particularly in body folds, known as acanthosis nigricans, which often indicate insulin resistance and should be taken seriously.
Understanding these symptoms empowers individuals to seek timely medical advice, fostering early diagnosis and intervention.
Causes of Type 4 Diabetes

Identifying the underlying causes of Type 4 Diabetes provides valuable insights into prevention and management strategies. Key contributors include:
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of diabetes can elevate the likelihood of developing insulin resistance and related health issues, emphasizing the need for vigilance among those with a genetic background.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor for developing insulin resistance and Type 4 Diabetes, highlighting the need for effective weight management strategies.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle often leads to weight gain and decreased insulin sensitivity, underscoring the importance of regular physical activity for overall health.
- Age: The risk of insulin resistance tends to increase with age, particularly for individuals over 45 years old, making it crucial for older adults to monitor their metabolic health closely.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and fluctuations in hormone levels can affect insulin sensitivity, contributing to the onset of Type 4 Diabetes.
Distinguishing Type 4 Diabetes from Type 2 Diabetes
While Type 2 Diabetes is well-known and primarily associated with lifestyle factors, Type 4 Diabetes introduces a nuanced perspective by emphasizing the interplay of insulin resistance and cognitive function. The key differences include:
- Mechanisms: Type 2 Diabetes typically develops due to obesity and lifestyle choices, whereas Type 4 Diabetes acknowledges the critical role of brain health and hormonal changes in regulating insulin sensitivity.
- Management Strategies: Individuals with Type 4 Diabetes may require a more comprehensive approach that includes cognitive assessments alongside traditional diabetes management strategies, allowing for tailored interventions.
Understanding these distinctions is vital for developing effective treatment plans that cater to individual needs and circumstances.
The Role of Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and Type 2 Diabetes. Many individuals diagnosed with Type 4 Diabetes frequently exhibit features of metabolic syndrome, including:
- Increased Waist Circumference: A larger waist circumference often indicates visceral fat accumulation, closely linked to insulin resistance and its associated risks.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension commonly coexists with metabolic syndrome and presents an additional cardiovascular risk, necessitating comprehensive health management.
- Elevated Triglycerides and Low HDL Cholesterol: Abnormal lipid profiles contribute to the overall risk of cardiovascular complications associated with Type 4 Diabetes, emphasizing the need for lifestyle modifications.
Addressing metabolic syndrome is critical for managing Type 4 Diabetes and preventing long-term health complications, reinforcing the importance of a holistic approach to treatment.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Type 4 Diabetes

Implementing intentional lifestyle changes can have a profound impact on the management of Type 4 Diabetes. Key strategies include:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activities, such as walking, swimming, or strength training, enhances insulin sensitivity, aids in weight management, and promotes overall cardiovascular health.
- Balanced Diet: A well-rounded diet rich in whole foods—including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains—can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of complications associated with Type 4 Diabetes.
- Managing stress is important because chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Integrating mindfulness techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can significantly assist in alleviating stress and improving emotional health.
Effective Blood Sugar Management
Managing blood sugar levels is paramount for individuals with Type 4 Diabetes. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can help identify patterns and inform necessary adjustments to diet and lifestyle. Collaborating with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan tailored to individual needs is highly recommended. This plan may include medication adjustments, dietary modifications, and exercise regimens based on blood sugar responses, ensuring a proactive approach to health.
Diagnosis of Type 4 Diabetes
Diagnosing Type 4 Diabetes typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests to assess blood sugar levels. Common diagnostic tests include:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test: This test measures blood sugar levels after fasting for at least eight hours, providing insights into insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test assesses blood sugar levels before and after consuming a sugary drink, helping to determine how well the body processes glucose.
- A1C Test: This test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months, indicating long-term glucose control and the effectiveness of management strategies.
These tests help healthcare providers establish an accurate diagnosis and create an appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Diet Recommendations for Type 4 Diabetes
A well-structured diet is crucial for managing Type 4 Diabetes effectively. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Incorporating High-Fiber Foods: Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits are excellent sources of fiber that can help stabilize blood sugar levels and support digestive health.
- Limiting Added Sugars: Reducing the intake of foods and beverages high in added sugars can prevent spikes in blood glucose levels, promoting overall health and well-being.
- Focusing on Healthy Fats: Including sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, can improve heart health and provide essential nutrients, aiding in blood sugar control.
- Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks can help maintain hydration and support metabolic processes, enhancing overall well-being.
Complications of Type 4 Diabetes
If left unmanaged, Type 4 Diabetes can lead to serious and potentially life-threatening complications. These complications may include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Individuals with Type 4 Diabetes are at increased risk of heart disease and stroke due to the effects of insulin resistance on blood vessels.
- Kidney Damage: Diabetic nephropathy may occur as a result of elevated blood sugar levels and poor circulation, leading to significant health concerns.
- Nerve Damage: Peripheral neuropathy can result in pain, tingling, or numbness in the extremities, impacting mobility and overall quality of life.
- Eye Damage: Diabetic retinopathy can cause vision problems, and if left untreated, may lead to blindness, underscoring the importance of regular eye examinations.
- Foot Complications: Poor circulation and nerve damage can lead to infections, ulcers, and even amputations in severe cases, emphasizing the necessity of foot care.
Being proactive in managing Type 4 Diabetes can help mitigate these risks and improve overall health, highlighting the importance of regular monitoring and effective lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Understanding Type 4 Diabetes is essential for effective management and prevention of serious complications. By making informed lifestyle choices, focusing on a balanced diet, and collaborating closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can take proactive steps toward better health and well-being. Emphasizing regular monitoring, proper nutrition, and physical activity can significantly influence blood sugar levels and enhance overall quality of life.
For those seeking affordable medication options, Better You Rx offers a range of treatments, including Ozempic, to help manage diabetes effectively. By prioritizing your health through access to cheap drugs and meds from Canada, you can take control of your diabetes management journey and improve your overall quality of life. Explore the benefits of a pharmacy-affiliated website dedicated to providing you with the medications you need to thrive.