Managing diabetes effectively requires constant awareness of blood sugar levels. Traditionally, checking glucose levels involved multiple daily finger pricks. While effective, this method can be inconvenient, painful, and prone to missed readings.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have revolutionized diabetes care by offering a more convenient, comprehensive, and accurate way to track blood sugar levels. This article explores the benefits of CGMs, how they work, and why they are becoming an essential tool for diabetes management.
What Are Continuous Glucose Monitors?
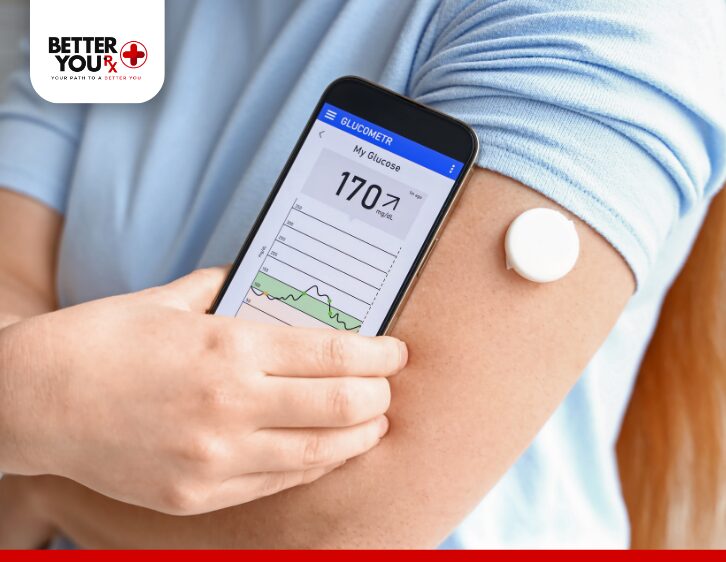
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) are wearable tools that track glucose in real time, day and night. They consist of three main components:
- Sensor: Inserted just under the skin, it measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid (the fluid between cells).
- The transmitter: relays sensor data to a receiver or compatible smartphone app.
- Receiver or App: Displays the glucose readings and trends.
Unlike traditional blood glucose meters, which provide a single snapshot, CGMs provide a continuous stream of data, offering valuable insights into glucose fluctuations.
How CGMs Work
Once the sensor is placed, it continuously monitors glucose levels, typically for 7–14 days, depending on the device. Data is transmitted to a compatible device, such as a smartphone or a dedicated reader, where users can view trends, set alerts, and make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
Key Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitors

1. Real-Time Glucose Tracking
CGMs offer continuous glucose readings, reducing or eliminating the need for finger sticks. This continuous monitoring allows for timely interventions, such as adjusting insulin doses or consuming carbohydrates when blood sugar levels drop.
2. Improved Glycemic Control
By displaying glucose trends, CGMs help users identify patterns, such as spikes after meals or drops during exercise. This insight enables better decision-making and promotes stable blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications like hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
3. Early Warnings and Alerts
CGMs can be programmed to alert users when glucose levels are too high or too low. These warnings provide an opportunity to take corrective action before symptoms escalate, enhancing safety, especially during sleep or physical activity.
4. Reduced Need for Finger Pricks
Although occasional finger sticks may still be required for calibration, CGMs drastically reduce the need for traditional glucose testing. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who find finger pricks painful or inconvenient.
5. Comprehensive Data Insights
CGMs track glucose levels 24/7, providing a more detailed picture of how various factors—diet, exercise, stress, and medications—affect blood sugar. This information empowers users and healthcare providers to optimize diabetes management plans.
6. Enhanced Quality of Life
The convenience of CGMs allows users to focus more on living their lives and less on the burden of frequent testing. The freedom from constant finger pricks and the confidence of having real-time data contribute to improved overall well-being.
Who Can Benefit from CGMs?

CGMs are suitable for:
- Individuals with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes who require frequent glucose monitoring.
- Those experiencing frequent episodes of hypoglycemia or unawareness of low blood sugar symptoms.
- People seeking tighter glucose control or struggling to identify patterns with traditional testing methods.
Popular CGM Devices
A variety of CGM systems exist, each offering distinct features and capabilities. Popular options include:
- Dexcom G6: Known for its accuracy, easy-to-use app, and compatibility with insulin pumps.
- Freestyle Libre: Offers a compact design and budget-friendly options, requiring a quick scan for glucose readings.
- Medtronic Guardian Connect: Features advanced predictive alerts and integration with insulin pump systems.
Integrating CGMs into Diabetes Management
Using a CGM is not just about tracking glucose—it’s about leveraging the data to improve overall diabetes care. Here’s how to maximize the benefits:
- Work with Healthcare Providers: Collaborate with your doctor or diabetes educator to analyze CGM data and refine your treatment plan.
- Set Realistic Goals: Use CGM insights to set achievable glucose targets and gradually work towards better control.
- Combine with Lifestyle Changes: Complement CGM data with a diabetes-friendly diet, regular exercise, and stress management for holistic care.
Overcoming Common Concerns
While CGMs offer numerous advantages, some individuals may have reservations, such as:
- Cost: CGMs can be expensive without coverage, but many find the investment worthwhile for the convenience and improved outcomes.
- Skin Irritation: Some users experience mild irritation at the sensor site, which can often be minimized with proper care and placement techniques.
- Learning Curve: Adjusting to a CGM may take time, but most users find the benefits outweigh the initial challenges.
The Role of CGMs in Preventing Complications
Consistent glucose monitoring reduces the risk of long-term complications, such as nerve damage, cardiovascular issues, and vision problems. CGMs are particularly beneficial for preventing severe hypoglycemia, a life-threatening condition that can occur unexpectedly.
Final Thoughts
Continuous Glucose Monitors are transforming the way diabetes is managed, offering unparalleled convenience, accuracy, and insights. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for years, CGMs can significantly enhance your ability to control blood sugar levels and improve your quality of life.
By embracing this technology and using it alongside a comprehensive diabetes care plan, you can take control of your health and reduce the risks associated with uncontrolled blood sugar.