How Diabetics Should Treat Cuts and Scrapes
For individuals living with diabetes, managing even minor injuries like cuts and scrapes is more than just a matter of first aid. Diabetes affects the body’s ability to heal, and cuts, scrapes, or other wounds can quickly become serious if not treated properly. High blood sugar levels can impair circulation, nerve function, and immune response, all of which play a critical role in wound healing. Therefore, it’s essential for diabetics to take extra precautions when dealing with cuts and scrapes to prevent infection, promote faster healing, and avoid complications.
In this article, we’ll explore the best practices for treating cuts and scrapes when living with diabetes, the potential risks of delayed healing, and the steps you can take to ensure your skin stays healthy and protected.
Why Diabetes Affects Wound Healing
Before diving into the steps for treating cuts and scrapes, it’s important to understand why diabetes makes wound healing more challenging. There are a few key factors that contribute to this:
- Poor Blood Circulation: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, leading to poor circulation. Reduced blood flow to the skin and tissues can make it harder for the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. Without proper circulation, minor injuries can become more prone to infection and take longer to heal.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): People with diabetes may experience nerve damage, particularly in the feet and hands. This condition, known as diabetic neuropathy, can reduce sensation in the affected areas. As a result, diabetics may not feel pain or notice cuts and scrapes right away. This delay in noticing an injury can increase the risk of infection and complications.
- Weakened Immune Response: Chronic high blood sugar can impair the function of white blood cells, which are responsible for fighting off infections. A weakened immune system means that cuts and scrapes may become infected more easily and take longer to heal.
- Increased Risk of Infection: Diabetes can increase the susceptibility to infections due to poor circulation and a compromised immune system. Bacteria can easily enter the body through open wounds, leading to more serious infections that could spread to other areas of the body.
Steps to Properly Treat Cuts and Scrapes for Diabetics

While cuts and scrapes are common and often minor, diabetics must take extra care to treat them properly to avoid complications. Here are the steps that should be followed:
1. Clean the Wound Thoroughly
The first and most important step in treating any cut or scrape is to clean the wound. Carefully wash the affected area with mild soap and water. Avoid using hydrogen peroxide or alcohol directly on the wound, as these can irritate the skin and slow down the healing process. Instead, opt for a gentle antiseptic solution that can clean the wound without causing damage to healthy tissue.
2. Control Bleeding
If the wound is bleeding, apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth or sterile gauze to help stop the bleeding. Elevating the injured area above the heart may also help reduce blood flow to the site of the wound, which can help control bleeding. Once the bleeding has ceased, move on to the next step.
3. Apply an Antibiotic Ointment
To prevent infection, apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment, such as Neosporin or a similar product, to the cleaned wound. This helps protect the area from bacteria and promotes faster healing. Ensure the ointment does not contain any ingredients that may irritate the skin, especially if you have sensitive skin.
4. Cover the Wound with a Sterile Bandage
After applying the antibiotic ointment, cover the wound with a clean, sterile bandage or dressing. Keeping the wound covered not only protects it from dirt and bacteria but also helps to maintain a moist environment, which can speed up the healing process. Be sure to change the bandage daily or whenever it becomes wet or dirty.
5. Monitor for Signs of Infection
For individuals with diabetes, infection is a significant concern when treating wounds. It’s essential to keep an eye on the wound for any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pus. If the wound begins to show any of these signs, or if the area becomes painful, seek medical attention immediately. An infection that isn’t treated promptly can lead to more serious complications, including cellulitis (a skin infection), abscesses, or, in extreme cases, the need for amputation.
6. Elevate the Injured Area
If possible, elevate the injured area above the heart to reduce swelling and improve circulation. Elevating the injury may help ensure that blood and nutrients reach the affected area, which can promote healing.
7. Check Blood Sugar Levels Regularly
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is critical when healing wounds, as high blood sugar can slow down the body’s natural healing process. Keep your blood sugar within the target range set by your healthcare provider, as this can help your body heal more effectively. If you notice your blood sugar levels are high, consider adjusting your diet or insulin regimen in consultation with your healthcare provider.
8. Stay Hydrated and Nourished
Proper nutrition and hydration play a role in wound healing. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly those that support skin health like vitamin C and zinc, can help your body repair itself. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to help support the healing process and keep your skin moisturized. A well-balanced diet will also help you maintain a healthy weight, which can positively impact blood sugar levels.
Potential Complications from Cuts and Scrapes in Diabetics
While treating cuts and scrapes in diabetics is essential for preventing infection and promoting healing, there are a few complications that can arise if proper care is not taken. Some of these include:
- Infections: As mentioned, diabetics are more prone to infections due to poor circulation and a weakened immune system. Infections can develop quickly and spread if not treated promptly. In severe cases, untreated infections can lead to sepsis or gangrene, which may require hospitalization or surgery.
- Delayed Healing: High blood sugar levels can interfere with the body’s natural healing process, leading to delayed wound healing. Even minor injuries can take much longer to heal in diabetics, which can increase the risk of complications.
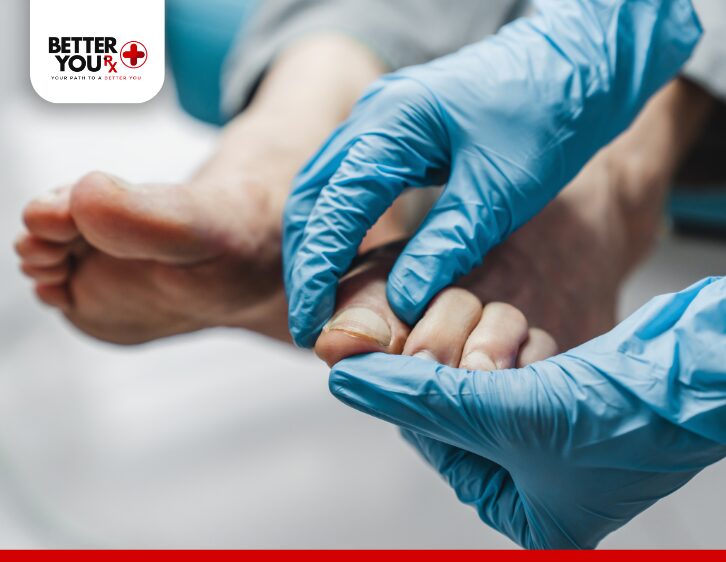
- Chronic Wounds: If a wound doesn’t heal properly, it may become a chronic wound. Diabetics are more prone to developing chronic wounds, especially on their feet, where nerve damage and poor circulation can make it harder for the body to repair itself. Chronic wounds may require professional medical treatment and could lead to long-term complications, including amputation in extreme cases.
When to Seek Medical Help

It’s important for individuals with diabetes to be proactive about seeking medical attention if they experience a cut or scrape that does not heal properly. If you notice any of the following symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider immediately:
- Signs of infection (redness, swelling, warmth, or pus)
- Wounds that are not healing after a few days
- Pain that does not improve or worsens
- A wound that has become larger or deeper
Prompt medical attention can help prevent serious complications and ensure that the wound heals as efficiently as possible.
Conclusion: Prevention and Vigilance are Key
Diabetes requires extra vigilance when it comes to treating cuts and scrapes. By following proper wound care steps, maintaining good blood sugar control, and monitoring for signs of infection, diabetics can reduce the risk of complications and promote faster healing. Regular visits to your healthcare provider for check-ups and foot exams are essential for maintaining overall health and preventing serious complications from minor injuries.
If you’re living with diabetes, don’t hesitate to take the necessary precautions when dealing with cuts and scrapes. Proper wound care is crucial for your long-term health and well-being, and by following these steps, you can protect your body from infection and ensure faster, more effective healing.