SAVE 10% OFF First Order With Coupon Code: happyhealth
Showing 157–168 of 717 results
-
Buy Desonide Cream from Canada
Original price was: $66.00.$44.95Current price is: $44.95.Desonide Cream functions by suppressing the immune response in the skin, leading to reduced itching, redness, and inflammation. It is well-suited for short-term treatment and management of mild to moderate skin conditions. When applied to the affected skin area, desonide interacts with skin cells to diminish the overactive inflammatory processes and relieve discomfort.
This medication is typically easy to apply and is ideal for treating sensitive skin areas, including the face and skin folds where milder corticosteroids are required. It is especially useful for managing flare-ups, allowing for a return to comfort and the healing of the skin.
-
-
-
Buy Dexilant from Canada
$246.99Dexlansoprazole is prescribed to manage gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition characterized by the backflow of stomach acid causing heartburn and potential harm to the esophagus (the tube connecting the throat and stomach). Dexlansoprazole is employed to alleviate GERD symptoms, promote esophageal healing, and safeguard against additional esophageal damage.
-
-
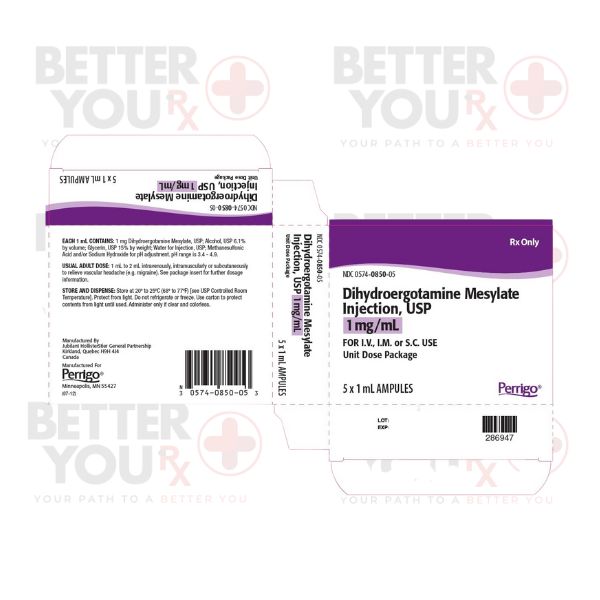
Buy Dihydroergotamine (DHE) Injection from Canada
Original price was: $342.00.$104.99Current price is: $104.99. -
Buy Dihydroergotamine Injection from Canada
Original price was: $86.63.$53.73Current price is: $53.73.Dihydroergotamine (DHE) Injection is a medication used to treat certain types of headaches, such as migraines and cluster headaches. It belongs to a class of drugs known as ergot alkaloids and works by narrowing the blood vessels in the head, thereby alleviating the intense pain associated with these conditions.
-
Buy Dilantin from Canada
$38.88 – $39.98Phenytoin is employed to manage specific types of seizures and to manage and prevent seizures that might arise during or following brain or nervous system surgery. Phenytoin is categorized as an anticonvulsant medication, and its mechanism of action involves the reduction of abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
-
Buy Dilantin from Canada
$45.99 – $53.99Dilantin functions by prolonging the inactivation of sodium channels in neuronal membranes, hence stabilizing the threshold against excitability triggered by excessive stimulation. By modifying the conductance among sodium channels, phenytoin prevents the spread of disruptive electrical charges in the brain which causes seizures. It’s essential for managing a stable level of Dilantin as its therapeutic window is narrow, and both underdose and overdose can cause issues.
This medication is crucial for individuals who suffer from epileptic conditions, offering a chance at normalcy by controlling seizures. It’s also sometimes used for treating trigeminal neuralgia and preventing seizures during or after neurosurgery.
-
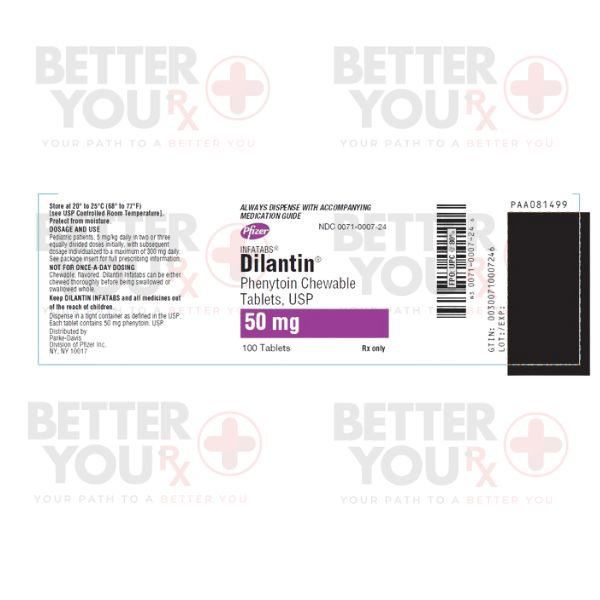
Buy Dilantin Infatabs Tablets from Canada
Original price was: $85.00.$51.99Current price is: $51.99.Phenytoin is employed to manage specific types of seizures and to manage and prevent seizures that might arise during or following brain or nervous system surgery. Phenytoin is categorized as an anticonvulsant medication, and its mechanism of action involves the reduction of abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
-
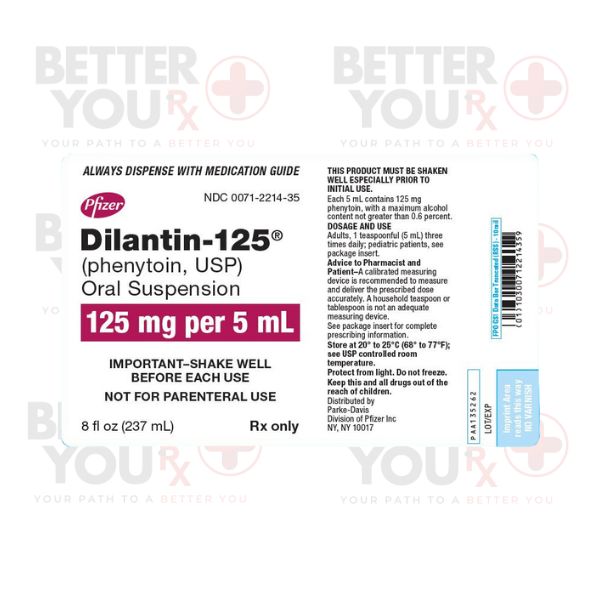
Buy Dilantin Suspension from Canada
Original price was: $85.00.$38.88Current price is: $38.88.Phenytoin is employed to manage specific types of seizures and to manage and prevent seizures that might arise during or following brain or nervous system surgery. Phenytoin is categorized as an anticonvulsant medication, and its mechanism of action involves the reduction of abnormal electrical activity in the brain.
-
Buy Diltiaz TZ from Canada
$139.00Diltiaz TZ combines the therapeutic effects of different drug components that work synergistically to control blood pressure and improve cardiac function. This medication balances the dilation of blood vessels and modulates sodium and potassium excretion to maintain heart health and regulate fluid retention.